아스파탐
|
|
아스파탐 속성
- 녹는점
- 242-248 °C
- 알파
- 15.5 º (c=4, 15N formic acid)
- 끓는 점
- 436.08°C (rough estimate)
- 밀도
- 1.2051 (rough estimate)
- 굴절률
- 14.5 ° (C=4, 15mol/L Formic Acid)
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 물과 에탄올(96%)에 조금 녹거나 약간 녹으며, 헥산과 염화메틸렌에는 거의 녹지 않습니다.
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- pKa 3.19±0.01 (H2O t=25.0 I=0.100(NaCl))(Approximate);7.87±0.02(H2O t=25.0 I=0.100(NaCl))(Approximate)
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 냄새
- 무취와 달콤한 맛
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- pH(8g/l, 25℃) : 4.5~6.0
- 수용성
- 포름산, 디메틸설폭사이드에 용해됩니다. 물과 에탄올에 거의 용해되지 않습니다.
- Merck
- 14,839
- BRN
- 2223850
- 시퀀스
- H-Asp-Phe-OMe
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 강한 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다.
- InChIKey
- IAOZJIPTCAWIRG-QWRGUYRKSA-N
- LogP
- 0.542 (est)
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 22839-47-0(CAS DataBase Reference)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 안전지침서 | 22-24/25 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| WGK 독일 | 2 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | WM3407000 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS 번호 | 29242990 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 22839-47-0(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | TDLo orl-wmn: 3710 mg/kg:SKN AIMEAS 104,207,86 |
아스파탐 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
아스파탐은 합성 감미료의 일종인 아스파틸-페닐알라닌-1-메틸 에스터의 이름으로, 일반 설탕인 자당의 약 200배의 단맛을 낸다. 대표적인 아미노산계 합성 감미료로 그 사용 폭이 매우 넓다.용도
고감미 감미료 중 설탕과 가장 비슷한 맛이 날뿐 아니라 설탕의 200분의 1 정도만 사용하면 되기 때문에, 많은 식품에 설탕 대용의 저칼로리 감미료로 쓰이고 있다. 특히, 다이어트 콜라와 같은 저가당 식품에 많이 쓰인다.순도시험
(1) 용상 : 이 품목 1g을 0.2N 염산으로 녹여 100mL로 하였을 때, 무색 징명하여야 한다.
(2) 액성 : 이 품목 0.8g을 물에 녹여 100mL로 한 수용액의 pH는 4.5~6.0이다.
(3) 비선광도 : 이 품목 2g을 정밀히 달아 15N 개미산용액에 녹인 다음 정확히 50mL로 한 액을 30분이내에 선광도를 측정하고 다시 건조물로 환산할 때, 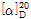 =+12.5~+17.5°이어야 한다.
=+12.5~+17.5°이어야 한다.
(4) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(5) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(6) 5-벤질-3,6-디옥소-2-초산피페라진 : 이 품목 10mg을 정밀히 달아 테프론마개가 있는 작은 유리병(약 3mL)에 취하고 실리레이숀시액 1mL를 가하여 밀봉하고 진탕한 후 80℃항온조내에서 30분간 가열한 다음 유리병을 꺼낸 후 15초간 진탕, 실온으로 냉각한다. 따로, 표준용액 3mL를 작은 유리병에 취하여 수욕상에서 증발건고시킨 다음 실리레이숀시액 1mL를 가하여 검체와 같은 조작을 행한다. 이를 가스크로마토그래피에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.5% 이하이어야 한다.
조작조건
주 입 기 : 마이크로텍 220 또는 이와 동등한 것이 부착된 것.
칼 럼 : 내경 3~4mm, 길이 2m의 유리관
칼럼충전제 : 80~100메쉬의 슈펠코포트 또는 이와 동등한 가스크로마토그래피용 담체에 대해서 3%되는 양의 OV—1을 입힌다.
검 출 기 : 수소염이온화 검출기(FID)
주입구온도 : 200℃
칼럼온도 : 200℃
검출기온도 : 275℃
캐리어가스 및 유량 : 질소가스를 사용한다. 5-벤질-3,6-디옥소-2-초산피페라진이 7~9분에서 검출되도록 유량을 조정한다.
시 액
실리레이숀시액 : N,O-비스(트리메틸실릴)아세트아미드, 디메틸포름아미드 3 : 2를 용량비로 혼합한다. 사용시 조제한다.
표준용액 : 5-벤질-3,6-디옥소-2-초산피페라진 표준품 25mg을 정밀히 달아 50mL 플라스크에 취하고 메탄올에 녹여 50mL로 한다. 이 액 10mL를 100mL 플라스크에 취해 메탄올로 100mL로 채운다.
(7) 투과도 : 이 품목을 2N 염산으로 1% 용액을 만들어 1cm셀에 넣어 분광광도계로 2N 염산을 대조액으로 하여 430nm에서 흡광도를 측정할 때, 그 흡광도는 0.022 이하이어야 한다.
확인시험
(1) 이 품목 10mg에 물 3mL 및 닌히드린․히드린단틴시액(닌히드린 2g을 취하여 디메틸설폭시드 75mL를 가하여 녹인 다음 히드린단틴 62mg을 가하여 녹이고 4M 초산리티움완충액(pH 9.0)을 가하여 100mL로 한 액) 2mL를 가하여 가열할 때, 흑자색을 나타낸다.
(2) 이 품목 약 20mg을 메탄올 1mL에 녹이고 염산히드록실아민으로 포화시킨 메탄올 0.5mL를 가한 다음 혼합하고 여기에 5N 수산화칼륨메탄올용액 0.3mL를 가한다. 이 혼합액을 끓을 때까지 가열하고 냉각시킨 다음 1N 염산으로 pH를 1.0~1.5로 조절한 다음 염화제이철용액(1→100) 0.1mL를 가할 때, 암적색을 나타낸다.
정량법
이 품목을 약 0.3g을 정밀히 달아 개미산 3mL를 가하여 용해한 후 초산 50mL를 가한 다음 즉시 0.1N 과염소산용액으로 적정한다(지시약 : α-나프톨벤제인시액 0.5mL). 종말점은 액의 갈색이 녹색으로 변하는 점으로 한다. 같은 방법으로 공시험하여 보정하고 다시 건조물로 환산한다.
0.1N 과염소산용액 1mL = 29.431mg C14H18N2O5
강열잔류물
이 품목의 강열잔류물은 0.2% 이하이어야 한다.
개요
Aspartame is the most popular artificial sweetener in the United States. It is sold as sweeteners such as NutraSweet and Equal, but it is also incorporated into thousands of food products.화학적 성질
Aspartame (N-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester, 3-amino-N-(a-carbomethoxy- phenethyl)-succinamic acid-N-methyl ester) is an intense sweetener widely used in foods and beverages. Its solubility in water is approximately 10 g/L at room temperature. Aspartame is not fully stable under common processing and storage conditions of foods and beverages with the highest stability around pH 4.3. Aspartame is about 200 times sweeter than sucrose with a clean, but slightly lingering sweetness. It is used as the single sweetener, but often also in blends with other intense sweeteners owing to synergistic taste enhancement and taste quality improvement often seen in such blends.In the European Union, aspartame is approved as E 951 for a large number of food applications. In the United States, it is approved as a multipurpose sweetener for food and beverage uses and it is also approved in many other countries.
역사
Aspartame was discovered accidentally in 1965 during a search for drugs to treat gastric ulcers. James M. Schlatter, an organic chemist working for G. D. Searle & Company, was using aspartyl-phenylalanine methyl ester (aspartame) in a synthesis procedure and inadvertently got some of the compound on his hands.용도
Aspartame is a high-intensity sweetener that is a dipeptide, provid- ing 4 cal/g. it is synthesized by combining the methyl ester of phenylalanine with aspartic acid, forming the compound n-l-alpha- aspartyl-l-phenylalanine-1-methyl ester. it is approximately 200 times as sweet as sucrose and tastes similar to sugar. it is compara- tively sweeter at low usage levels and at room temperature. its mini- mum solubility is at ph 5.2, its isoelectric point. its maximum solubility is at ph 2.2. it has a solubility of 1% in water at 25°c. the solubility increases with temperature. aspartame has a certain insta- bility in liquid systems which results in a decrease in sweetness. it decomposes to aspartylphenylalanine or to diketropiperazine (dkp) and neither of these forms is sweet. the stability of aspartame is a function of time, temperature, ph, and water activity. maximum stability is at approximately ph 4.3. it is not usually used in baked goods because it breaks down at the high baking temperatures. it contains phenylalanine, which restricts its use for those afflicted with phenylketonuria, the inability to metabolize phenylalanine. uses include cold breakfast cereals, desserts, topping mixes, chew- ing gum, beverages, and frozen desserts. the usage level ranges from 0.01 to 0.02%.정의
ChEBI: A dipeptide composed of methyl L-phenylalaninate and L-aspartic acid joined by a peptide linkage.생산 방법
Aspartame is produced by coupling together L-phenylalanine (or Lphenylalanine methyl ester) and L-aspartic acid, either chemically or enzymatically. The former procedure yields both the sweet aaspartame and nonsweet β-aspartame from which the α-aspartame has to be separated and purified. The enzymatic process yields only α-aspartame.제조 방법
By coupling the amino acids L-phenylalanine and L-aspartic acid, and the esterification of the carboxyl group of the phenylalanine moiety to produce the methyl ester. This esterification can occur before or after coupling. The crystallized slurry is centrifuged and the resulting “wet-cake” is washed to remove impurities.일반 설명
Asp-Phe methyl ester (aspartame, APM, ASP), a dipeptide ester, is made up of phenyl alanine and aspartic acid. Its genotoxic effects have been investigated. Its interaction with certain hydrocolloids has been studied.Pharmaceutical Applications
Aspartame is used as an intense sweetening agent in beverage products, food products, and table-top sweeteners, and in pharmaceutical preparations including tablets, powder mixes, and vitamin preparations. It enhances flavor systems and can be used to mask some unpleasant taste characteristics; the approximate sweetening power is 180–200 times that of sucrose.Unlike some other intense sweeteners, aspartame is metabolized in the body and consequently has some nutritive value: 1 g provides approximately 17 kJ (4 kcal). However, in practice, the small quantity of aspartame consumed provides a minimal nutritive effect.
Safety Profile
Human systemic effects byingestion: allergic dermatitis. Experimental reproductiveeffects. When heated to decomposition it emits toxicfumes of NOx.환경귀착
Aspartame is nontoxic. However, individuals with the rare, genetic disease, phenylketonuria (PKU), cannot properly metabolize phenylalanine. Such individuals are detected by testing at birth and placed on special low-phenylalanine diets to control their blood phenylalanine concentrations. Thus, PKU individuals need to be aware that aspartame is a source of phenylalanine.신진 대사 경로
The rate of aspartame degradation is faster in a phosphate buffer solution than in a citrate buffer solution at the same pH and buffer concentration. The primary mechanism by which aspartame degrades, the formation of diketo piperazine, involves the nucleophilic attack of carbonyl by the free amine, which requires proton transfer.저장
Aspartame is stable in dry conditions. In the presence of moisture, hydrolysis occurs to form the degradation products L -aspartyl-Lphenylalanine and 3-benzyl-6-carboxymethyl-2,5-diketopiperazine with a resulting loss of sweetness. A third-degradation product is also known, β-L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester. For the stability profile at 258℃ in aqueous buffers.Stability in aqueous solutions has been enhanced by the addition of cyclodextrins, and by the addition of polyethylene glycol 400 at pH 2. However, at pH 3.5–4.5 stability is not enhanced by the replacement of water with organic solvents.
Aspartame degradation also occurs during prolonged heat treatment; losses of aspartame may be minimized by using processes that employ high temperatures for a short time followed by rapid cooling.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container, in a cool, dry place.
비 호환성
Differential scanning calorimetry experiments with some directly compressible tablet excipients suggests that aspartame is incompatible with dibasic calcium phosphate and also with the lubricant magnesium stearate. Reactions between aspartame and sugar alcohols are also known.Regulatory Status
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe and in the USA. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral powder for reconstitution, buccal patch, granules, syrups, and tablets). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.아스파탐 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
아스파탐 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +86-13474506593 +86-13474506593 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 874 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12456 | 58 |
| Sinoway Industrial co., ltd. | 0592-5800732; +8613806035118 |
xie@china-sinoway.com | China | 992 | 58 |
| Sichuan HongRi Pharma-Tech Co.,Ltd | +86-028-64841719 +8618980456393 |
daisy@enlaibio.com | China | 1369 | 58 |
| Across Biotech Jinan Co LTD | +8613031735486 |
frank@acrossbiotech.com | China | 105 | 58 |
| Wuhan Quanjinci New Material Co.,Ltd. | +8615271838296 |
kyra@quanjinci.com | China | 1532 | 58 |
| Hebei Jingbo New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +8619931165850 |
hbjbtech@163.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Shandong Juchuang Chemical Co., LTD | +86-18885615001 +86-18885615001 |
admin@juchuangchem.com | China | 387 | 58 |
| airuikechemical co., ltd. | +undefined86-15315557071 |
sales02@airuikechemical.com | China | 994 | 58 |
| Hebei Saisier Technology Co., LTD | +86-18400010335 +86-13102810335 |
admin@hbsaisier.cn | China | 690 | 58 |







