L-베타-아스파라긴
|
|
L-베타-아스파라긴 속성
- 녹는점
- 235 °C (dec.) (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 244.01°C (rough estimate)
- 알파
- 34.5 º (c=10, 2N HCl)
- 밀도
- 1,543g/cm
- 굴절률
- 1.4880 (estimate)
- 저장 조건
- Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature
- 용해도
- 메탄올, 에탄올, 에테르, 벤젠에는 거의 녹지 않습니다. 산과 알칼리에 용해됩니다.
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 2.17(at 20℃)
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 냄새
- 살짝 달콤한 맛
- 수용성
- H2O: 20 g/L (20 oC) , 투명, 무색
- 감도
- Hygroscopic
- Merck
- 14,837
- BRN
- 1723527
- 안정성
- 안정적이지만 습기에 민감할 수 있습니다. 강한 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다.
- LogP
- -3.820
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 70-47-3(CAS DataBase Reference)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 20/21/22-36/37/38 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 24/25-36-26 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 3-10 | ||
| TSCA | Y | ||
| 위험 등급 | IRRITANT | ||
| HS 번호 | 29241900 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 70-47-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-01953 |
L-베타-아스파라긴 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
순도시험
(1) 용상 : 이 품목 1g을 물 50mL에 녹인 액은 무색이며 징명하여야 한다.
(2) 액성 : 이 품목 1g을 물 100mL에 녹인 액의 pH는 3.5~5.5이어야 한다.
(3) 비선광도 : 이 품목 10g을 정밀히 달아 6N 염산에 녹여 100mL로 하여 이 액의 선광도를 측정하고, 다시 건조물로 환산할 때, 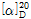 =+33.0~+36.5°이어야 한다.
=+33.0~+36.5°이어야 한다.
(4) 염화물 : 이 품목 0.07g을 취하여 염화물시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 0.01N 염산 0.2mL에 대응하는 양 이하이어야 한다.
(5) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(6) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 5.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
확인시험
(1) 이 품목의 수용액(1→1,000) 5mL에 닌히드린용액(1→50) 1mL를 가하고 수욕상에서 3분간 가열할 때 자색을 나타낸다.
(2) 이 품목 0.1g에 수산화나트륨용액(1→10) 5mL를 가하고 수욕상에서 가온할 때 발생하는 가스(NH3)는 물에 적신 적색리트머스지를 청색으로 변화한다.
정량법
이 품목 약 0.3g을 정밀히 달아 개미산 3mL에 녹이고 빙초산(비수적정용) 50mL를 가하고 0.1N 과염소산용액으로 적정한다(지시약 : 크리스탈바이올렛․빙초산시액 1mL). 종말점은 액의 자색이 청색을 지나 녹색으로 변하는 점이다. 따로 같은 방법으로 공시험을 한다.
0.1N 과염소산용액 1mL = 13.212mg C4H8N2O3
강열잔류물
이 품목의 강열잔류물은 0.1% 이하이어야 한다.
개요
Asparagine (abbreviated as Asn or N) is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids on Earth. It has carboxamide as the sidechain's functional group. It is not an essential amino acid. Its codons are AAU and AAC.The amino acid L-asparagine is a structural analog of L-aspartic acid, where the side chain of the carboxylic acid moiety is amidated, to give a terminal amine group. This renders L-asparagine neutral at physiological pH. The amide group of asparagine is derived from glutamate, in the reaction of aspartate and glutamine in the presence of ATP to yield asparagine and glutamate. In vivo, asparagine is hydrolyzed to aspartate and NH4+ by asparaginase. Asparagine is also an important amino acid in glycopeptide bonds, via N-glycosyl linkages to the sugar rings.
화학적 성질
White crystal or crystalline powder with a slightly sweet taste. Slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol and ether, it often exists as a monohydrate, and it is a rhombic hemihedral crystals. The melting point is 234-235°C , and the aminocarbonyl reaction is carried out by co-heating with sugar, which can form special aroma substances. The best recrystallization method is water, followed by ethanol. In case of alkali hydrolysis into aspartic acid. Heating its aqueous solution also decomposes. Natural products exist in various legumes and the like.물리적 성질
Solubility 3.11 (28 ℃) g/100 g H2O, pI 5.41, dissociation constants: pK1 2.02, pK2 8.8.출처
Dietary sourcesAsparagine is not essential for humans, which means that it can be synthesized from central metabolic pathway intermediates and is not required in the diet. Asparagine is found in :
Animal sources : dairy, whey, beef, poultry, eggs, fish, lactalbumin , sea food
Plant sources : asparagus, potatoes, legumes, nuts, seeds, soy, whole grains.
Biosynthesis
The precursor to asparagine is oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is converted to aspartate using a transaminase enzyme. The enzyme transfers the amino group from glutamate to oxaloacetate producing α- ketoglutarate and aspartate. The enzyme asparagine synthetase produces asparagine, AMP, glutamate, and pyrophosphate from aspartate, glutamine, and ATP. In the asparagine synthetase reaction, ATP is used to activate aspartate, forming β-aspartyl-AMP. Glutamine donates an ammonium group, which reacts with β-aspartyl-AMP to form asparagine and free AMP.
역사
Asparagine was first isolated in 1806, under a crystalline form, by French chemists Louis Nicolas Vauquelin and Pierre Jean Robiquet (then a young assistant) from asparagus juice, in which it is abundant — hence, the name they chose for that new matter — becoming the first amino acid to be isolated.A few years later, in 1809, Pierre Jean Robiquet again identified, this time from liquorice root, a substance with properties he qualified as very similar to those of asparagine, that Plisson in 1828 identified as asparagine itself.
용도
L-asparagine has been used:to identify and quantify free amino acids released upon oxidation of proteins and peptides by hydroxyl radicals.
to study the effects of amino acids in promoting food consumption in Drosophila melanogaster.
to study non-enzymatic gluconeogenesis.
L-Asparagine is used in cell culture media and is a component of MEM non-essential amino acids solution.
L-Asparagine has been shown to enhance ornithine decarboxylase activity in cultured human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells and in cultured IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells. Spore germination in Bacillus subtilis has been increased in the presence of L-asparagine.
An isoxazoline RGD mimic platelet GPIIb/IIIa antagonist has been prepared by chiral synthesis with L-asparagine as a starting material. L-Asparagine has been utilized in the synthesis of 4-azalysine building blocks for application to combinatorial chemistry.
생산 방법
A simple synthesis of L -asparagine starts from L -aspartic acid which is esterified to the b-methyl ester followed by treatment with ammonia.정의
ChEBI: L-asparagine is an optically active form of asparagine having L-configuration. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a human metabolite, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite, a mouse metabolite and a plant metabolite. It is an aspartate family amino acid, a proteinogenic amino acid, an asparagine and a L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate base of a L-asparaginium. It is a conjugate acid of a L-asparaginate. It is an enantiomer of a D-asparagine. It is a tautomer of a L-asparagine zwitterion.Biological Functions
Asparagine is a dietarily dispensable amino acid synthesized from aspartate and glutamine. Asparagine has three major functions: 1) incorporation into amino acid sequences of proteins; 2) storage form for aspartate (is a required precursor for synthesis of DNA, RNA and ATP); and 3) source of amino groups for production of other dispensable amino acids via trasaminases.The nervous system requires asparagine. It also plays an important role in the synthesis of ammonia.
The addition of N-acetyl glucosamine to asparagine is performed by oligosaccharyltransferase enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum. This glycosylation is important both for protein structure and protein function.
Safety Profile
When heated to decomposition emits toxic fumes of NoxPurification Methods
Likely impurities are aspartic acid and tyrosine. Crystallise it from H2O or aqueous EtOH. It slowly effloresces in dry air. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 p 1856 1961, Beilstein 4 IV 3005.]L-베타-아스파라긴 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
L-베타-아스파라긴 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingdao Trust Agri Chemical Co.,Ltd | +8613573296305 |
aroma@qdtrustagri.com | China | 165 | 58 |
| DONBOO AMINO ACID COMPANY | +8613063595538 |
donboo@donboo.com | China | 9365 | 58 |
| Hebei Guanlang Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +8619930503252 |
daisy@crovellbio.com | China | 5964 | 58 |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 |
info@fdachem.com | China | 7534 | 58 |
| Hebei Saisier Technology Co., LTD | +86-18400010335 +86-13102810335 |
admin@hbsaisier.cn | China | 565 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +86-13474506593 +86-13474506593 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 848 | 58 |
| Ouhuang Engineering Materials (Hubei) Co., Ltd | +8617702722807 |
admin@hbouhuang.com | China | 738 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | 571-85586718 +8613336195806 |
sales@capotchem.com | China | 29797 | 60 |
| Shanghai Daken Advanced Materials Co.,Ltd | +86-371-66670886 |
info@dakenam.com | China | 15371 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21695 | 55 |







