A carbohydrate compound is an organic substance composed of three elements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. From the chemical structure, the carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones and their multimers. Sugar is widely distributed in the plant kingdom and is the main constituent of plants. It plays an important role in the physiological and biochemical processes of plants. According to its structure, it can be divided into monosaccharides (including glucose, fructose, galactose, etc.), disaccharides (including sucrose, maltose, lactose, etc.) and polysaccharides (including starch, glycogen, muscle glycogen, etc.). Monosaccharide is the simplest carbohydrate, polyhydroxy aldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone that can no longer be hydrolyzed.
Maltose: Overview and Dietary Implications
Maltose is essential for brewing, baking, and energy production, with dietary implications emphasizing the importance of enzymes in maltose digestion.
Oct 25,2024 CarbohydratesDextran: Application, pharmacokinetics and toxicity
Dextran is a complex branched glucan (polysaccharide derived from the condensation of glucose), originally derived from wine, and dextran chains are of varying lengths.
Apr 25,2023 CarbohydratesHydroxypropyl methyl cellulose: Application, metabolism and pharmacokinetics
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is a modification of alkali cellulose, and it find use in in the food, drug, and the dietary supplement industries.
Mar 24,2023 Carbohydrates3-O-Benzyl-1,2,5,6-di-O-isopropylidene-alpha-D-glucofuranose: Preparation and Applications in Chemical Biology
3-O-Benzyl-1,2:5,6-di-O-isopropylidene-alpha-D-glucofuranose (3-O-B-DIP-alpha-D-Glu) is a sugar derivative of glucose with a benzyl group attached to the 3-position of the sugar ring.
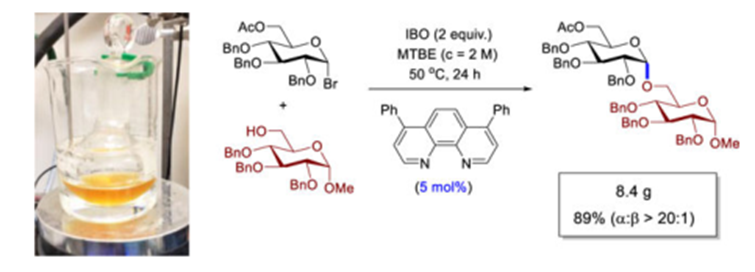
Mar 10,2023 CarbohydratesApplication of O-Phenanthroline
O-Phenanthroline is an organic compound with the molecular formula C12H8N2. The solid is white crystal and dissolved in water to form a light yellow to yellow solution.
Feb 15,2022 Carbohydrates