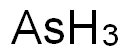비소
|
|
비소 속성
- 녹는점
- 817 °C(lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 613 °C(lit.)
- 밀도
- 5.727 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
- 증기압
- 1Pa at 280℃
- 용해도
- insoluble in H2O
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 색상
- 실버에서 블랙으로
- Specific Gravity
- 5.727
- 냄새
- 냄새 없는
- 비저항
- 33.3 μΩ-cm
- 수용성
- 불용성
- 감도
- Air Sensitive
- Merck
- 13,802
- 노출 한도
- TLV-TWA 0.2 mg(As)/m3 (ACGIH), 0.5 mg (As)/m3 (MSHA), 0.01 mg(As)m3 (OSHA); ceiling 0.002 mg(As)/m3/15 min (NIOSH); carcinogenicity: Human Sufficient Evidence (IARC).
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 산, 산화제, 할로겐과 호환되지 않습니다. 열과 공기에 민감합니다.
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7440-38-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 1 (Vol. 23, Sup 7, 100C) 2012
- NIST
- Arsenic(7440-38-2)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 23/25-50/53-36/38-22-45-52/53-51/53 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 20/21-28-45-60-61-26-53 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1558 6.1/PG 2 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | CG0525000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 10 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1 | ||
| 포장분류 | II | ||
| HS 번호 | 28048000 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7440-38-2(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | Human exposure occurs occupationally and via food, tobacco smoke, ambient air, and water. Three major groups of arsenic compounds have been defined on the basis of biological considerations: inorganic arsenicals; organic arsenicals; and arsine (gas). The comparative toxicity of these groups is dependent upon the route of exposure and their solubilities; the more quickly absorbed compounds have lower LD50. Arsenic is readily absorbed by the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems and is concentrated in the skin, hair, and nails (Aldrich-Mees’ lines). The cellular toxicity of arsenic is related to reactions with SH-containing mitochondrial enzymes that result in impaired respiration. Arsenic may also compete with phosphate during oxidative phosphorylation. | ||
| IDLA | 5 mg As/m3 | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-01933 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 97-1-119 | ||
| 중점관리물질 필터링 | 별표1-122 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 유독물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 비소 또는 그 화합물과 비소화합물을 0.1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
비소 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
비소는 은회색(황색)과 흑갈색의 동소체를 가지며 마늘냄새가 나는 고체로 원자번호는 33번이다. 비소의 지각 농도는 높지 않아 1.8ppm이며 물, 알카리에는 녹지 않으나 질산에는 용해한다.개요
비소(Arsenic)는 다양한 형태의 화합물로 환경 중에 널리 분포하는 금속물질로서 강한 독성을 가지고 있는 주요 환경오염물질이다. 비소 화합물은 산소(O), 염소(Cl), 및 황(S)과 결합한 무기 비소 화합물과 탄소(C)와 수소(H)와 결합한 유기 비소 화합물로 나뉘며 비소의 인체에 대한 위해성은 이온의 상태나 화합물의 형태에 따라 서로 다른 것으로 알려져 있다.용도
인류가 비소를 발견하면서부터 금세기 중반까지 비소에 대한 이용은 갈수록 더 광범해져 의약, 농업, 목축업, 임업 및 기타 공업 부문까지 그 이용이 증대되고 있으며 주용도는 반도체, 합금첨가 원소, 특수 유리나 납의 경화제 등이다. 의약 방면에서는 비소 화합물로 매독·빈혈을 치료하고 신체를 강하게 하는 약제로 사용하는 외에도 Fowler액으로 풍습증(류머티즘), 백혈병, 마른버짐 등을 치료했다.개요
Arsenic is a metalloid of the nitrogen group. Two allotrope forms of elemental arsenic have been reported: yellow arsenic and grey arsenic, the latter being usually the more stable form. Arsenic readily oxidises in air to arsenic trioxide (As2O3). Arsenic is mostly found either in its native state or as arsenic sulfide in the form of realgar (As4S4) or orpiment (As2S3). Arsenic can exist in three different valence states (zerovalent, trivalent and pentavalent). Arsenic forms covalent bonds with carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. The toxicity varies widely and depends on the physical state of the compound and its absorption/elimination rate. Trivalent arsenics (As(III)) are derivatives of the arsenous acid (H2AsO3-arsenite) and arsenic trioxide (AsO3). Examples of pentavalent arsenic (As(V)) include derivatives of the arsenic acid (H3AsO4 -arsenate). Organic arsenic-based compounds, that is, compounds containing arsenic-carbon bonds, are usually less toxic than their inorganic counterparts. This is mainly due to their quicker excretion from the human body. Arsenic is known to be one of the most toxic heavy metals. Compounds containing arsenic have a long history of use as poisons, but they also have a long historical medicinal use.화학적 성질
Arsenic (As) is the third element in Group VA of the periodic table. Elemental arsenic can be found in two solid forms: yellow and gray or metallic, with specific gravities of 1.97 and 5.73, respectively (CRC, 1999). Gray arsenic is the ordinary stable form. Arsenic compounds can be categorized as inorganic and organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain an arsenic–carbon bond while organic compounds do.
물리적 성질
Arsenic is classed as a semimetal, meaning that it is neither a metal like aluminum or lead,nor quite a nonmetal such as oxygen, sulfur, or chlorine. Arsenic’s main allotrope is a silverygray,brittle, metal-like substance. Its other two isotopes are unstable crystalline substances.Gray arsenic exhibits an unusual property in that its boiling point (614°C) is lower than itsmelting point (817°C). As its temperature changes, it sublimates, which means it goes fromthe solid state, skipping the liquid state, into a vapor state. Cooling the vapor of sublimation,the black allotrope condenses out and in turn changes from the black to the gray allotrope. Ifyellow arsenic is rapidly cooled from its sublimation point, yellow arsenic will condense outand will not revert back to gray arsenic upon cooling.
The following information is for the gray semimetal form of arsenic only. Its melting pointis 817°C, its sublimation point varies between 613°C and 814°C depending on the atmosphericpressure, and its density is 5.776 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are a total of 35 isotopes of arsenic, ranging from As-60 to As-92, withhalf-lives spanning from a few nanoseconds to 80 days. Although some references claimthere are no stable isotopes of arsenic, arsenic-75 is classed as a stable isotope thatmakes up 100% of arsenic found in the Earth’s crust.Origin of Name
Derived either from the Latin word arsenicum or the Greek word arsenikon, both meaning a yellow pigment. It is possible that the Arabic word azzernikh was also an ancient name for arsenic.출처
Arsenic is the 53rd most abundant element and is widely distributed in the Earth’s crust.It occurs naturally in several minerals, but high-grade deposits are rare. Most of the mineralsand ores that contain arsenic also contain other metals. Some major sources of arsenic are theminerals orpiment, scherbenkobalt, arsenopyrite, niccolite, realgar, gersdorffite, and smaltite.In addition, most sulfide ores of other metals also contain some arsenic. The three major mineralsthat produce arsenic are: realgar (arsenic monosulfide, AsS), orpiment (arsenic trisulfide,As2S2), and arsenopyrite (iron arsenosulfide, FeAsS).Today, most arsenic is recovered as a by-product from the smelting of nickel, copper, iron,and tin. It is also recovered from the flue dust of copper- and lead-smelting furnaces.
Characteristics
Arsenic in the elemental form is a brittle, grayish crystal that becomes darker when exposedto air. It is seldom found in the pure elemental form but rather in minerals (compounds). Ithas a long history of use as a poison, and many alchemists were poisoned when using it intheir attempts to produce gold from base metals.Arsenic has limited commercial use.
용도
Arsenic is a brittle solid with a metallic coloring that ranges from silver to gray. It is a naturally occurring element found in the earth’s crust, and it cycles rapidly through water, land, air, and living systems. Exposure to it occurs through ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact.The arsenic metalloid is used for hardening copper and lead alloys (HSDB, 2005). It is also used in glass manufacturing as a decolorizing and refining agent, as a component of electrical devices in the semiconductor industry, and as a catalyst in the production of ethylene oxide. Arsenic compounds are used as a mordant in the textile industry, for preserving hides, as medicinals, pesticides, pigments, and wood preservatives. The production of chromate copper arsenate (CCA), a wood preservative, accounts for approximately 90% of the domestic arsenic consumption (ATSDR, 2007). However, production of this preservative is being phased out. The uses of inorganic arsenical compounds (e.g., lead arsenate) as pesticides were voluntarily cancelled by the industry during late 1980s and early 1990s. A majority of organoarsenicals are used on cotton and turf as herbicides. disodium methanearsenate (DSMA), monosodium methanearsenate (MSMA), and calcium methanearsenate (CAMA) continue to be used as contact herbicides.
정의
A toxic metalloid element existing in several allotropic forms; the most stable is a brittle gray metal. It belongs to group 15 (formerly VA) of the periodic table. Arsenic is found native and in several ores including mispickel (FeSAs), realgar (As4S3), and orpiment (As2S3). The element reacts with hot acids and molten sodium hydroxide but is unaffected by water and acids and alkalis at normal temperatures. It is used in semiconductor devices, alloys, and gun shot. Various compounds are used in medicines and agricultural insecticides and poisons.Symbol: As; m.p. 817°C (gray) at 3 MPa pressure; sublimes at 616°C (gray); r.d. 5.78 (gray at 20°C); p.n. 33; r.a.m. 74.92159.
일반 설명
A grayish metallic solid that turns black upon exposure to air. Insoluble in water. Toxic by ingestion.공기와 물의 반응
Turns black on exposure to air. Insoluble in water.반응 프로필
Arsenic reacts incandescently with bromine trifluoride, even at 10°C [Mellor 2:113 1946-47]. Causes bromoazide to explode upon contact. Ignites if ground up together with solid potassium permanganate [Mellor 12:322 1946-47]. Is oxidized by sodium peroxide with incandescence [Mellor 2:490-93 1946-47]. A combination of finely divided Arsenic with finely divided bromates (also chlorates and iodates) of barium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, or zinc can explode by heat, percussion, and friction [Mellor 2:310 1946-47]. Bromine pentafluoride reacts readily in the cold with Arsenic. Ignition usually occurs. Reacts vigorously with fluorine at ordinary temperatures [Mellor 9:34 1946-47].위험도
Most of the compounds of arsenic are toxic when in contact with the skin, when inhaled,or when ingested. As with arsenic’s cousin phosphorus above it in group 15 of the periodictable, care must be taken when using arsenic. The compound arsenic trioxide (As2O3), anexcellent weed-killer, is also carcinogenic. Copper acetoarsenite, known as Paris green, is usedto spray cotton for boll weevils. A poisonous dose of arsenic as small as 60 milligrams can bedetected within the body by using the Marsh test.공업 용도
Arsenic (symbol As) is a soft, brittle, poisonouselement of steel-gray color and metallic luster.In atomic structure it is a semimetal, lackingplasticity, and is used only in alloys and incompounds. The bulk of the arsenic used isemployed in insecticides, rat poisons, and weedkillers, but it has many industrial uses, especiallyin pigments. It is also used in poisongases for chemical warfare.Metallic arsenic is stable in dry air. Whenexposed to humid or moistened air, the surfacefirst becomes coated with a superficial goldenbronze tarnish, which on further exposure turnsblack. On heating in air arsenic will vaporizeand burn to As2O3.Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen producing liver tumors. Poison by subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic skin and gastrointestinal effects by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Flammable in the form of dust when exposed to heat or flame or by chemical reaction with powerful oxidizers such as bromates, chlorates, iodates, peroxides, lithium, NC4, m 0 3 , Khfn04, Rb2C2, AgN04, NOCl, IF5, CrO3, CIF3, Cl0, BrF3, BrFj, BrN3, RbGBCH, CsC3BCH. Slightly explosive in the form of dust when exposed to flame. When heated or on contact with acid or acid fumes, it emits highly toxic fumes; can react vigorously on contact with oxidizing materials. Incompatible with bromine azide, dirubidium acetylide, halogens, palladium, zinc, platinum, NCh, AgNO3, CrO3, Na2O2, hexafluoroisopropylideneamino lithum.잠재적 노출
Arsenic compounds have a variety of uses. Arsenic and its compounds are used as an alloy additive, in electronic devices; in veterinary medicines; in agriculture as insecticides, herbicides, larvicides, and pesticides. Some arsenic compounds are used in pigment production; the manufacture of glass as a bronzing or decolorizing agent; the manufacture of opal glass and enamels, textile printing; tanning, taxidermy, antifouling paints; to control sludge formation in lubricating oils. Metallic arsenic is used as an alloying agent for heavy metals; and in solders, medicines, herbicides. EPA has estimated that more than 6 million people living within 12 mi of major sources of copper, zinc, and lead smelters-may be exposed to 10 times the average United States atmospheric levels of arsenic. The agency says that 40,000 people living near some copper smelters may be exposed to 100 times the national atmospheric average.Carcinogenicity
Arsenic and inorganic arsenic compounds are known to be human carcinogens based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans.환경귀착
Trivalent arsenic exerts its toxic effects mainly by disrupting ATP production by inhibiting lipoic acid, which is a cofactor for pyruvate as well by replacing phosphate which uncouples oxidation phosphorylation. This inhibits the electron transport chain in the mitochondria and the ultimate synthesis of ATP. Hydrogen peroxide production is also increased, which, it is speculated, has potential to form reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. These metabolic interferences lead to death from multisystem cell death and organ failure. The activity of enzymes is due to the functional groups on amino acids such as the sulfhydryl group on cysteine or coenzymes such as lipoic acid, which has vicinal thiol groups. Trivalent inorganic arsenicals readily react with sulfhydryl groups such as cysteine creating a strong complex between arsenic and vicinal sulfhydryl reagents. These actions inhibit not only the formation of Acetyl-CoA but also the enzymes succinic dehydrogenase and pyruvate. Arsenite inhibits the binding of steroids to the glucocorticoid receptor, but not other steroid receptors. The probable mechanism of toxicity of pentavalent inorganic arsenate is its reduction to a trivalent form, arsenite, which is more toxic than the arsenate. Thus, a variety of mechanisms lead arsenic to impair cell respiration and subsequently diminish ATP formation.운송 방법
UN1558 Arsenic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.비 호환성
Incompatible with strong acids; strong oxidizers; peroxides, bromine azide, bromine pentafluoride, bromine trifluoride; cesium acetylene carbide, chromium trioxide; nitrogen trichloride, silver nitrate. Can react vigorously with strong oxidizers (chlorine, dichromate, permanganate). Forms highly toxic fumes on contact with acids or active metals (iron, aluminum, zinc). Hydrogen gas can react with inorganic arsenic to form highly toxic arsine gas.폐기물 처리
Elemental arsenic wastes should be placed in long-term storage or returned to suppliers or manufacturers for reprocessing. Arsenic pentaselenide-wastes should be placed in long-term storage or returned to suppliers or manufacturers for reprocessing. Arsenic trichloride: hydrolyze to arsenic trioxide utilizing scrubbers for hydrogen chloride abatement. The trioxide may then be placed in long-term storage. Arsenic trioxide: long-term storage in large shiftproof and weatherproof silos. This compound may also be dissolved, precipitated as the sulfide and returned to the suppliers. Arsenic-containing sewage may be decontaminated by pyrolusite treatment. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.비소 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
Quartz cotton
Quartz disc, fused, 76.2 (3.0 in) dia x 3.18mm (0.13in) thick
Quartz tubing, fused, 12.7mm (0.5in) OD for compression type fittings
카본블랙
삼산화 비소
준비 용품
비소 공급 업체
글로벌( 143)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 |
info@fdachem.com | China | 18229 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29914 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28180 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22968 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-61398051 +8613650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39916 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34572 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 9126 | 58 |
| changzhou huayang technology co., ltd | +8615250961469 |
2571773637@qq.com | China | 9821 | 58 |
| Hebei Duling International Trade Co. LTD | +8618712993135 |
sales01@hbduling.cn | China | 15741 | 58 |
비소 관련 검색:
삼산화 비소 오산화 비소 삼염화 비소 포타슘 헥사플루오로아르세네이트(v) 아비산 나트륨 비소 황화합물 아르사닐산 다이소듐 아르세네이트 칠수화물 비소
Sodium cacodylate trihydrate
4-DIMETHYLAMINOAZOBENZENE-4'-ARSENIC ACID
ZINC GRANULATED ARSEN FREE
ARSENIC - 15% HCL 100ML
ARSENIC - AS2O3 AS AS+3, 99.999%, 2% HCL 500ML
ARSENIC - 15% HCL 500ML
ARSENIC - AS METAL, 99.999%, 2% HNO3 100ML
ARSENIC ICP/DCP STANDARD SOLUTION (HNO3)
ARSENIC, AAS STANDARD SOLUTION, SPECPURE®, AS 1000µG/ML