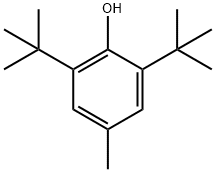
Butylated Hydroxytoluene: uses and side effects
Apr 22,2024
Description
Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) have been widely used for many years as antioxidants to preserve and stabilize the freshness, nutritive value, avour and color of foods and animal feed products.

Uses
Butylated hydroxytoluene, a cresol derivative, is an additive used as an antioxidant in foods such as packet cake mixes, potato crisps, salted peanuts, and dehydrated mashed potatoes. In March 1990, the Danish Product Register included 440 products containing butylated hydroxytoluene; the content was below 50 ppm in 66% of these products; the main categories were paints/lacquers and hardeners for paints, glues, and fillers[1].
BHT can also improve the stability of pharmaceuticals, fat-soluble vitamins, and cosmetics. The service life of rubber, elastomers, and plastics is increased by the addition of BHT, and from such use, BHT may be present as an indirect food additive. Approximately 40 countries reportedly permit using BHT as a direct or indirect food additive. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) permits BHA and BHT as food additives. Food-grade BHA referred to as 2(3)-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, is generally a mixture of greater than 85% 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (3-BHA) and 15% or less 2-tert-butyl-4- hydroxyanisole (2-BHA), while food-grade BHT, which is 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene, is not less than 99% (w/w) pure.
Genotoxicity studies
BHT did not cause DNA damage in Bacillus subtilis or mutation in Salmonella typhimurium. It did not induce chromosomal aberrations in plants or mutation and chromosomal aberrations in Drosophila melanogaster[2]. In one study, it was reported to be mutagenic to cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells in an exogenous metabolic system. The binding of BHT to the DNA of the liver of rats exposed in vivo has been reported, but no adduct was identified. Moreover, BHT was negative for DNA repair in isolated hepatocytes. BHT did not induce micronuclei in bone marrow or dominant lethal mutations in mice. BHT also exhibited no evidence of mutagenicity in the Salmonella/microsome mutagenesis assay or the adult rat liver epithelial cell/hypoxanthine±guanine phosphoribosyl transferase mutagenicity assay. The weight of evidence, therefore, supports the conclusion that BHT is not genotoxic.
Side effects
Some animal studies have shown BHT as an endocrine disruptor that has toxic effects on the liver, lungs, kidneys, blood, and reproductive systems. As an endocrine disruptor, it can impact testosterone levels as well as affect sperm quality. Another reason BHT isn’t good for you is that it might cause enlargements in the liver, inflammatory effects in the lungs, renal dysfunction, and a decrease in potassium levels.
References
[1] "Butylated Hydroxytoluene.”Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition) (2016): 1108.
[2] G.M Williams, J Whysner, M.J Iatropoulos . “Safety Assessment of Butylated Hydroxyanisole and Butylated Hydroxytoluene as Antioxidant Food Additives.” Food and Chemical Toxicology 37 9 (1999): Pages 1027-1038.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The Antioxidant of Butylated Hydroxytoluene Nov 17, 2022
The passage introduces the antioxidant of Butylated Hydroxytoluene.
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene - Properties and Application Mar 30, 2020
Butylated hydroxytoluene are also be named as 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol, Antioxidant 264, 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-methylphenol, BHT, DBPC, dibutylhydroxytoluene. The Molecular Weight of BHT is 220.35.
- What is Butylated hydroxytoluene(BHT)? Feb 20, 2020
BHT, also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties.
Low-quality or decomposed material, however, often shows a dark orange-brown color or, in extreme cases of decay, a dark greenish color. In addition, it is slightly soluble in Chloroform, ethyl Acetate, and methanol.....
Apr 22,2024Organic Raw MaterialIn terms of abundance in the Earth's crust, the rarest metals are gold, platinum, osmium, iridium, palladium, ruthenium, rhodium, tellurium, and rhenium.....
Apr 22,2024Inorganic chemistryButylated Hydroxytoluene
128-37-0You may like
Butylated Hydroxytoluene manufacturers
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene
-

- $50.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-03
- CAS:128-37-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20Tons
- 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol
-

- $5.00 / 25kg
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:128-37-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 200mt/year
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-29
- CAS:128-37-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 10 tons