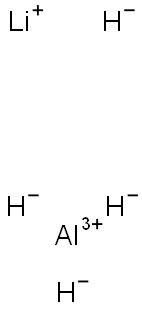Lithium Tetrahydridoaluminate:A powerful nucleophilic reducing agent
Oct 21,2023
Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, lithium aluminum hydride, lithium alanate, LiAlH4, is a fine crystalline powder. It is stable in the absence of moisture, but after some months at room temperature it becomes gray due to traces of elemental aluminum. This extremely slow decomposition hardly affects the reactivity of the product.

Reactions
On heating in the absence of air, decomposition starts at 125℃ with liberation of hydrogen. The first product is Li3AlH6, which itself decomposes above 200℃ into LiH, Ae, and H2; the ultimate decomposition products are LiAl and H2 (430℃). If LiAlH4 is heated in air, the liberated hydrogen ignites and burns quietly, and the metallic residue then burns with incandescence, whereby nitrogen also takes part in the reaction.
Moist air causes LiAlH4 to lose reactivity as a result of hydrolysis, but under normal conditions it is not spontaneously flammable. It reacts extremely violently with water. The liberated hydrogen (2.3 L/g at STP) usually ignites spontaneously because of the large heat of hydrolysis (DH0 298 = 714 kJ=mol).
Lithium aluminum hydride is soluble in various ethers, but not in hydrocarbons. It forms very stable solvates with some ethers and with tertiary amines; these solvates can very often be isolated. Some solvates are soluble in hydrocarbons.
Uses
Lithium aluminum hydride is a powerful nucleophilic reducing agent. It reduces almost all functional groups, although isolated double and triple bonds in alkenes and alkynes are generally not attacked. Bulk lithium aluminum hydride is used almost exclusively for the reduction of organic functional groups. The principal consumers are the organic chemical, pharmaceutical, and the flavoring and perfumery industries. Lithium aluminum hydride is more expensive than sodium borohydride and is mainly used when the reducing power of the latter is inadequate. Lithium aluminum hydride is used in industry mainly for the reduction of carboxylic acids and esters to alcohols, and of amides, imides, and nitriles to amines. Its powerful reducing properties are also used in the reduction of sterically hindered compounds.
It has the advantage over some other reducing agents of being very clean to use as the precipitated sludges from the hydrolysis of the aluminate complex are easily separated and there are no toxic or gaseous byproducts. Furthermore, it has the highest hydrogen content per unit mass of the commercially available complex hydrides. Lithium aluminum deuteride, LiAlD4 [14128- 54-2] (Chemetall), is also commercially available and is used for isotopic labelling of organic compounds with deuterium.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride: Lithium Storage Mechanism and its Synthesis Procedure Nov 5, 2024
Lithium Aluminum Hydride's diverse applications span battery technology, showcasing complex synthesis, storage mechanisms, and the quest for enhanced performance.
- Uses of Lithium aluminium hydride in organic chemistry Jan 27, 2022
Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAl H4), commonly abbreviated to LAH, is a powerful reducing agent used in organic chemistry.
- What is Lithium Aluminum Hydride? Dec 13, 2021
Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiAlH4. It is a grey solid. It was discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947.
Benzyl chloride can serve as a starting point for the preparation of benzal chloride and benzotrichloride, both of which are accessible by sidechain chlorination.....
Oct 21,2023Organic ChemistryZirconium hydride is used in the nuclear industry as a moderator for thermal neutrons, especially in light water reactors and fast breeder reactors.....
Oct 21,2023Reducing agentLithium Aluminum Hydride
16853-85-3You may like
Lithium Aluminum Hydride manufacturers
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:16853-85-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2025-09-26
- CAS:16853-85-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20Tons
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride
-

- $50.00 / 1KG
- 2025-09-25
- CAS:16853-85-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available