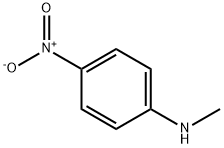
N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline: Physicochemical Properties, Degradation and Toxicity
Nov 6,2024
N-Methyl-p-nitroaniline is a brownish yellow prismatic crystal with a purple hue, with a melting point of 152°C. It is easily soluble in acetone and benzene, slightly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in water.

Physicochemical properties
N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline(MNA) has low solubility in water; 85 mg L-1 at 25 °C (Boddu et al., 2008a). While the chemical structure of MNA includes both hydrophilic (amino) and hydrophobic (nitro) moieties, the aqueous solubility of MNA is greatly reduced by the N-methyl substitution (Ahmed and Sandler, 2012). Reduction of MNA to N-methyl-p-phenylenediamine (MPD) has been reported in an ethanol-amended anaerobic fluidized bed bioreactor treating MNA and other co-contaminants, such as DNAN and perchlorate (Platten et al., 2013).1
Degradation
The aerobic degradation of N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline, a compound used to lower the melting temperature in the synthesis of insensitive explosives, has been successfully demonstrated by Pseudomonas sp. strain FK357 isolated from soil. This process marks a significant advancement as prior to this, only anaerobic biotransformation of N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline had been documented.
Toxicity
Classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Acute toxicity, Oral (Category 3), H301 Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure (Category 2), H373.
1. Boddu VM, Abburi K, Maloney SW, Damavarapu R. Physicochemical properties of an insensitive munitions compound, N-methyl-4-nitroaniline (MNA). J Hazard Mater. 2008;155(1-2):288-294.
References:
[1] VEERA M. BODDU . Physicochemical properties of an insensitive munitions compound, N-methyl-4-nitroaniline (MNA)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 155 1: 1-396. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.074.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline: properties, applications and safety Aug 29, 2023
N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline is used in organic synthesis, polymers, and explosives. It has limited solubility in water but dissolves in organic solvents. Safety precautions are necessary.
- What is N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline? Feb 24, 2020
N-methyl-4-nitroaniline(C7H8N2O2,MNA) appears as brownish-yellow prisms with violet reflex (from ethanol) or yellow powder with a melting point of 152 °C. N-methyl-4-nitroaniline is easily soluble in acetone and benzene.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringPolyethyleneimine enhances cancer therapy and gene delivery by overcoming drug resistance and cytotoxicity through targeted modifications for safer, effective treatments.....
Mar 8,2024APIN-Methyl-4-nitroaniline
100-15-2You may like
N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline manufacturers
- N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline
-

- $12.00 / 25KG
- 2025-12-15
- CAS:100-15-2
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200mt
- N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline
-

- $30.00 / 1KG
- 2025-06-27
- CAS:100-15-2
- Min. Order: 50KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- N-Methyl-4-nitroaniline
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-06-20
- CAS:100-15-2
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 20 tons