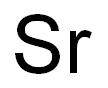Strontium Industrial Applications and Uses
Sep 25,2019
Strontium chemical symbol Sr, atomic number 38, and relative atomic mass (i.e., atomic weight) 87.62, is the fourth alkaline-earth metal, i.e., elements of group IIA of Mendeleev’s periodic chart. The word strontium comes from Strontian, a town in Scotland.Strontium is a hard, silvery-white metal when freshly cut, but it readily tarnishes in moist air, becoming yellowish due to the formation of the oxide. It resembles barium in its properties but is harder and less reactive. It has a low density (2540 kg.m–3), and a relatively Alkaline-Earth Metals 2634 Less Common Nonferrous Metals high melting point 770°C (1042 K). It has a face-centered cubic crystalline structure and decomposes water, evolving hydrogen and forming the hydroxide Sr(OH)2. Strontium fines such as powder, dust, and turnings are pyrophoric, i.e., they ignite spontaneously in air.

The element was first identified by the British chemist Adair Crawford in 1790 (Edinburgh, Scotland). Actually, he recognized a new heavy mineral (later named strontianite) that differed from the heavy barium sulfate barite. Later, in 1809, the metal was first isolated by the British chemist Sir Humphry Davy by performing molten-salt electrolysis of strontium chloride.
Industrial Applications and Uses
The strontium content in the lithosphere is ca. 370 mg/kg (i.e., ppm wt.), but, owing to its chemical reactivity, the metal does not occur free in nature. The chief strontium containing minerals are the sulfate celestite or celestine [SrSO4, orthorhombic] and the carbonate strontianite [SrCO3, orthorhombic], but strontium traces can also be found in calcium and barium-containing minerals. Nevertheless, strontium minerals rarely concentrate in large ore deposits, and the chief ore is only represented by celestite because there are no known economically workable strontianite deposits. However, strontium occurs widely dispersed in seawater and in igneous rocks as a minor constituent of rock-forming minerals.
The flame color of strontium has led to its extensive use in pyrotechnics for firework blends and also as a component in red emergency signal flares and on tracer bullets. It is also used as strontium carbonate for colored glass for cathodic ray television (CRT) tubes. Strontium ferrite is used for manufacturing small magnets for electric motors. Srontium titanate, SrTiO3, owing to its high refractive index and an optical dispersion greater than that of diamond, is used as an optical device. Strontium compounds have also been used as deoxidizers of nonferrous metals and alloys. The radionuclide 90Sr, with a half-life of 29 years, is a byproduct of nuclear fission and is easily recovered from spent nuclear fuel. This radionuclide is the best long-lived, high-energy pure beta emitter known (max. kinetic energy of the electrons is 546 keV). Hence it is used as a heat-generation source converted by the Peltier effect (i.e., thermoelectric) into electrical energy in SNAP (i.e., systems nuclear auxiliary power). Strontium metal is also sometimes used as a getter in electron vacuum tubes.
Industrial Preparation
After mining, the raw ore is finely crushed and ground and undergoes a froth flotation beneficiation process to concentrate and separate celestine from byproduct minerals (e.g., barite). Then, the concentrate ore is reduced by pyrolysis in a kiln to strontium sulfide (i.e., SrS or black ash). The black ash is then dissolved in pure water, and the aqueous solution is treated with sodium carbonate to precipitate the strontium-carbonate crystals. After the strontianite crystals are removed and dried, the strontianite undergoes a calcination, evolving carbon dioxide and giving anhydrous strontium oxide (i.e., SrO, strontia). Strontium metal can be obtained either by thermal reduction of this strontium oxide with molten aluminum in a vacuum or by fused strontium chloride electrolysis.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Strontium: Major Minerals, Chemistry properties and Reactions May 29, 2024
Strontium (Sr) is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element. It is a member of alkaline earth elements (Group 2) and occupies an intermediate position between Ca and Ba.
- How funny strontium flame test Jan 24, 2024
Positive result of a flame test for strontium (Sr), producing a red colour. This is due to the excitation of electrons in the strontium by the heat of the flame.
Films of platinum only two atoms thick supported by graphene could enable fuel cell catalysts with unprecedented catalytic activity and longevity, according to a study published recently by researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology....
Sep 25,2019Inorganic chemistryFrom a chemical point of view, niobium, despite its resemblance to tantalum, is less corrosion resistant in concentrated strong mineral acids. However, it remains chemically inert to several inorganic and organic corrosive chemicals below 1....
Sep 25,2019Analytical ChemistrySTRONTIUM
7440-24-6You may like