POLY(ACRYLIC ACID): Application, Synthesis and Hazard
Apr 13,2023
General description
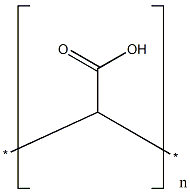
The POLY(ACRYLIC ACID) is a water-soluble polymer of acrylic acid and also soluble in some polar solvents, such as methanol, dioxane and ethylene glycol. Because the molecule contains a large number of carboxyl groups, it can react with alkali, alcohol and amine. And can also carry out dehydration, degradation and complexation reactions. It is widely used in coating, plastic, paper, textile, rubber, food, medicine, cosmetics, water treatment and other industries as thickener, dispersant, flocculant, adhesive and film-forming agent, etc. Its appearance is as follows:

Figure 1 Appearance of POLY(ACRYLIC ACID).
Chemical synthesis
The POLY(ACRYLIC ACID) can be synthesized according to the previous work [1]. Add deionized water into the polymerization kettle, heat it at 60~100 ℃, with dripping the mixed solution of ammonium persulfate and acrylic acid (prepared with deionized water) and stirring for 3~4h. Add 530kg of deionized water, 41kg of flat water and OS-15 into the polymerization kettle, and stir for dissolution. Afterwards, 4kg of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 68kg of mixed monomers (butyl acrylate, acrylonitrile) are add within 20min. Continue stirring for 15min, and slowly raise the temperature to 70 ℃. Stir at 80 ℃ for 1h. After the reaction, the reactant is cooled to about 40 ℃, stirred for 15min and filtered to remove impurities.
The product is polymerized by solution polymerization method, using acrylic acid as raw material, under the action of initiator. The polymerization of acrylic acid is fast and exothermic. In order to control the polymerization process, acrylic acid is usually mixed into an aqueous solution of less than 40%, and the polymerization temperature is usually controlled at 50~150 ℃ in the preparation of polyacrylic acid. The commonly used initiators are ammonium persulfate and sodium sulfite. In the polymerization process, a small amount of mercaptosuccinic acid and isopropanol are often added as polymerization inhibitors, and hydroquinone or catechol are used as polymerization inhibitors. Add a certain amount of stoichiometric deionized water into the reactor equipped with electric stirrer, reflux condenser, drip funnel and thermometer, and raise the reaction temperature to about 80 ℃.
The stoichiometric ammonium persulfate is prepared into a dilute solution with metered water and placed in a drip funnel on the polymerization reactor. The metered acrylic acid (AA) monomer is mixed with a certain amount of water and placed in another drip funnel on the polymerization reactor. When the water temperature in the reactor reaches the temperature required for the reaction, the acrylic monomer aqueous solution and the initiator ammonium persulfate aqueous solution shall be added dropwise, and the reaction temperature shall be controlled between 85 and 90 ℃, and the polymerization reaction shall be conducted for 3 to 5 h. Subsequently, white flocculation appears in the reaction. After washing with water, the product POLY(ACRYLIC ACID) is obtained.
Application
POLY(ACRYLIC ACID) is a generic term for organic polymer compounds synthesized using acrylic acid as the monomer, and it is an organic material. The polymer's viscosity and water absorbency are increased when it is cross-linked by a cross-linking agent, and because of this difference in properties, it is used in various applications such as paints, shampoos, and other daily necessities, and in additives for food and pharmaceuticals [2]. It can be used as an excellent suspending agent, emulsifier, transparent matrix of advanced cosmetics and pharmaceutical excipient matrix, and is also the most effective water-soluble thickener. It can also be used as a thickener and binder in toothpastes, and can be used in combination with other polymers. Meanwhile, it is also a common dispersant, which can disperse microcrystals or sediment of calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate and other salts in water without precipitation, so as to achieve the purpose of scale inhibition [3]. In addition to being used as scale inhibitor and dispersant in circulating cooling water system, it is also widely used in papermaking and textile, printing and dyeing, ceramics, coatings and other industries.
Hazard
There have been reports recently that cross-linked polyacrylic acid (POLY(ACRYLIC ACID)) can possibly cause serious lung disease [4]. Male F344 rats were administered low (0.2 mg/rat) and high (1.0 mg/ rat) doses of POLY(ACRYLIC ACID)intratracheally and were dissected 3 days, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after exposure to examine inflammatory and fibrotic responses in the lungs. There was a dose-dependent increase in the total cell count, neutrophil count, neutrophil percentage, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), surfactant protein D (SP-D), cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-1 and CINC-2 values in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from 3 days to at least 3 months after intratracheal administration of POLY(ACRYLIC ACID). Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in lung tissue was also persistently elevated from 3days to 6 months after exposure. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in BALF was elevated at 3 days and 1 month after exposure only in the high-dose group. Histopathological findings in lung tissue showed inflammatory and fibrotic changes from 3 days after administration, and we observed obvious inflammatory changes for up to 3 months and fibrotic changes for up to 6 months.
References
[1]Chen et al. Carbomer and its preparation method. CN 201310453464, 1 Jan 2014.
[2]Mun et al. On the role of specific interactions in the diffusion of nanoparticles in aqueous polymer solutions. Langmuir. 2014;30(1):308-317.
[3]Takeda et al. Dose–response relationship of pulmonary disorders by inhalation exposure to cross-linked water-soluble acrylic acid polymers in F344 rats. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022;19(1):27
[4]Higashi et al. Pulmonary disorder induced by cross-linked polyacrylic acid. Journal of Occupational health. 2022, 64(1): 12369.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Carbomer: A Critical Component in Modern Chemistry May 29, 2024
In the expansive field of polymer chemistry, carbomer stands out as a versatile and vital synthetic compound.
- Applications and Side effects of Carbomer Apr 14, 2022
Carbomer is a term used for a series of polymers primarily made from acrylic acid. Carbomers are white, fluffy powders but are frequently used as gels in cosmetics and personal care products.
- What is Poly(Acrylic Acid)(PAA)? Mar 12, 2021
Poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) is a polymer of acrylic acid, which has a carboxylic group on each monomer unit. This polymer becomes a polyelectrolyte in water via dissociation of the acid groups.
AZD3759 is a small molecule inhibitor of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) receptor tyrosine kinase. It is being developed as a potential treatment for non-small cell lung cancer.....
Apr 12,2023API2-Methyl-3-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propanal is a widely used commercially available fragrance material,and there is dermal exposure associated with its use.....
Apr 13,2023Flavors and fragrancesCarbomer
9007-20-9You may like
- Carbomer
-

- $16.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:9007-20-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000kg
- Carbomer940
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-30
- CAS:9007-20-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 56.0%-68.0%
- Supply Ability: 1000 KGS
- Carbomer
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-20
- CAS:9007-20-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 50000kg