The source and biological activity of Protocatechuic acid
Nov 21,2023
Introduction
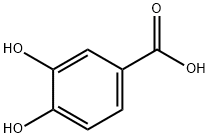
Protocatechuic acid (PCA), also known as 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. This compound is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H6O4. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea[1].

Source
Protocatechuic acid is widely distributed and present in most edible plants used in folk medicine. It is also a widespread compound in the human diet, present in bran, grain brown rice, and onion, especially in the scales. Protocatechuic acid is detected in many fruits, such as plums, gooseberries, grapes, nuts, and almonds. It is present in products of plant origin, such as olive oil or white wine. Protocatechuic acid is also found in many plants and spices, such as star anise, melissa, medical rosemary, cynamonowa, Hibiscus sabdariffa (roselle), Eucommia ulmoides (du-zhong), and Citrus microcarpa Bunge (calamondin). PCA content varies considerably depending on the type of food[2].
Biological activity
PCA has been reported for its potential action such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial activity, anticancer activity, antiulcer activity, antidiabetic activity, antiageing activity, antifibrotic activity, antiviral activity, anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic activity, antiatherosclerotic activity, cardiac activity, hepatoprotective activity, neurological and nephroprotective activity.
Protocatechuic acid inhibited low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation mediated by macrophage in an in vitro cell model. PCA reduced monocyte adhesion and NF-κB activation in vitro, decreased VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in vitro and in vivo, and inhibited the formation of early atherosclerotic lesions in the ApoE-deficient mouse model.PCA treatment significantly lowered serum marker enzymes and liver antioxidants of diabetic rats in inflammatory conditions[3]. Furthermore, it also reduced plasma C-reactive proteins and von Willebrand factor levels, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels in heart and kidney.
References
[1] Yoswaris Semaming. "Pharmacological properties of protocatechuic Acid and its potential roles as complementary medicine." Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2015): 593902.
[2] Kakkar, Sahil, and S. Bais. "A Review on Protocatechuic Acid and Its Pharmacological Potential." Isrn Pharmacology 2014(2014):952943.
[3] Gunawardena, Dhanushka, S. Govindaraghavan, and Gerald Münch. "Anti-inflammatory properties of cinnamon polyphenols and their monomeric precursors." Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease. (2014).
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is Protocatechuic acid? Jan 17, 2022
Protocatechuic acid has inhibitory effects on white and Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus A, Haemophilus influenzae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Proteus.
- Effects of Protocatechuic acid Sep 24, 2021
Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a simple phenolic acid, which is the precursor for the synthesis of other complex molecules, such as anthocyanin 3-O-β-D-glucoside and vanillin.
Terbinafine is an oral antifungal agent used to treat fungal infections of the hair, nails, and skin. It is also used to treat fungal infections of the scalp follicles in children at least 4 years old.....
Nov 21,2023Drugshe Lewis structure of O3 also consists of three oxygen atoms bonded at an angle of 116 degrees. There is one double bond and one single bond between the oxygen atoms (O).....
Nov 21,2023APIProtocatechuic acid
99-50-3You may like
- Acid phosphatases and Phosphatase, Acid from wheat germ
May 27, 2024
- The structure and Biological function of Cytochrome C
May 17, 2024
- Is CJC-1295 DAC same as CJC-1295?
May 16, 2024
Protocatechuic acid manufacturers
- Protocatechuic acid
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:99-50-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000kg
- 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
-

- $0.00 / 25Kg/Drum
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:99-50-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200mt/year
- Protocatechuic Acid
-

- $18.00 / 10kg
- 2024-05-10
- CAS:99-50-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.9
- Supply Ability: 5000