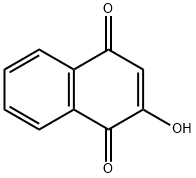
What is 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone?
Feb 14,2020
2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (HNQ, C10H6O3, CAS registry No. 83-72-7) is also called Lawsone, which is a white cubic crystal. Its melting point is 192-195 oC, and flash point is 192 oC. The solubility of HNQ is 2 g/L in water at 20 oC. It is stable, but it is combustible and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. So, it should kept tightly closed and store in a cool dry place.
HNQ is the principal natural dye ingredient contained at 1.0-1.4% in the leaves of Henna (Lawsonia inermis). It is an ancient red-orange dye. Henna has been used for more than 4000 years not only as a hair dye, but also as a body paint and tattoo dye[1]. Today, semi-permanent hair dyes containing Henna as well as its pure dye ingredient HNQ are widely used and have become increasingly popular due to their natural origin. Henna is used for hair dyeing at a rate of approximately 20 g per application, corresponding to 200–300 mg of pure HNQ. Hair dyes on the basis of pure HNQ typically contain concentrations of 1.20-1.5% HNQ. Thirty-five milliliters of the dye formulation are applied to the hair, corresponding to an amount of approximately 400 mg HNQ. Application of Henna or HNQ is followed by 30 min development and rinse off[2]. HNQ reacts chemically with the protein keratin in skin and hair via Michael addition, resulting in a strong permanent stain that lasts until the skin or hair is shed.
HNQ was reported to be a weak bacterial mutagen for Salmonella typhimurium strain TA98 or was more clearly mutagenic for strain TA 2637, both in the presence of metabolic activation. HNQ was unable to induce sex-linked recessive lethal mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. The available data suggest that the use of Henna or HNQ for hair dyeing presents no or negligible risk of genotoxicity to the consumer[2].
Inspection of the structure of HNQ shows the presence of keto-enol group that may be suited for hydrogen bonding with electronegative anions and a substrate for conjugate addition of strong nucleophiles such as cyanide which makes it a reasonable candidate as anion receptor, while the presence of naphthoquinone unit could be used as a signaling unit. Naphthoquinone is also redox active, suggesting that HNQ may be used as an electrochemical receptor for anions. Therefore, HNQ has been used as a sensitive colorimetric and electrochemical sensor for anions such as cyanide, acetate, fluoride and dihydrogen phosphate (DHP) in acetonitrile[3]. These anions cause a color change in HQN’s solution from yellow to orange-red. Other anions, such as chloride, bromide, iodide, perchlorate, do not show a significant change.
In organic chemistry, HQN can be used as Michael donor to participate in the asymmetric Michael addition to α,β-unsaturated acylphosphonates, generating the corresponding β-(3-hydroxy-1,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-substituted carboxylates in excellent yields with high levels of enantioselectivities (94 - >99% ee)[4]. Another example is the organocatalytic enantioselective Michael addition of 2-hydroxynaphthoquinones to nitroalkenes for the direct synthesis of chiral nitroalkylated naphthoquinone derivatives with good yields and excellent enantioselectivities (up to >99% ee)[5].

Fig 1. Chemical structure formula of 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
References
[1].Ashnagar, A.; Shiri, A., Isolation and characterization of 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (lawsone) from the powdered leaves of henna plant marketed in Ahwaz city of Iran. International Journal of ChemTech Research 1941, 3, 974-4290.
[2].Kirkland, D.; Marzin, D., An assessment of the genotoxicity of 2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, the natural dye ingredient of Henna. Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2003, 537 (2), 183-199.
[3].Hijji, Y. M.; Barare, B.; Zhang, Y., Lawsone (2-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) as a sensitive cyanide and acetate sensor. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2012, 169, 106-112.
[4].Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Song, H.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, C., Organocatalyzed Enantioselective Michael Addition of 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone to β,γ-Unsaturated α-Ketophosphonatesθ. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2011, 76 (10), 4119-4124.
[5].Zhou, W.-M.; Liu, H.; Du, D.-M., Organocatalytic Highly Enantioselective Michael Addition of 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinones to Nitroalkenes. Organic Letters 2008, 10 (13), 2817-2820.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
See also
7,9-Ditert-butyl-1-oxaspiro[4.5]deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione (C17H24O3, CAS registry No. 82304-66-3) is an oxaspiro compound that is 1-oxaspiro[4.5]deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione carrying two additional tert-butyl substituents at positions 7 and 9.....
Feb 13,2020Natural Products1,3-Difluorobenzene (C6H4F2, CAS registry No. 372-18-9) is also named as m-difluorobenzene, which is a clear colorless to yellowish liquid. Its melting point is -59 °C, boiling point is 83 °C and flash point is 2 oC.....
Feb 14,2020Pharmaceutical intermediates2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
83-72-7You may like
2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone manufacturers
- 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
-

- $5.00 / 25kg
- 2024-06-14
- CAS:83-72-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: ≥98%
- Supply Ability: 200mt/year
- 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
-

- $450.00 / 100kg
- 2024-06-14
- CAS:83-72-7
- Min. Order: 100kg
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 100Tons
- 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphoquinone
-

- $100.00 / 1bag
- 2023-09-14
- CAS:83-72-7
- Min. Order: 1bag
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 5000