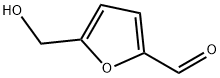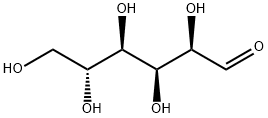
D(+)-Glucose synthesis
- Product Name:D(+)-Glucose
- CAS Number:50-99-7
- Molecular formula:C6H12O6
- Molecular Weight:180.16
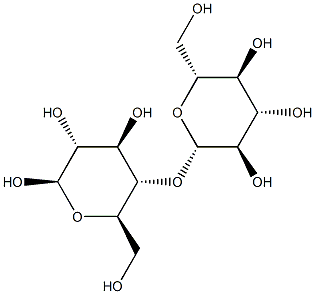
13360-52-6
0 suppliers
inquiry

50-99-7
975 suppliers
$6.00/25g
Yield:50-99-7 91.1%
Reaction Conditions:
with sulfuric acid in water at 130; pH=4; for 6 h;Kinetics;Catalytic behavior;Inert atmosphere;Sealed tube;pH-value;Temperature;
Steps:
Methods
The initial reaction solution, containing 0.1746 g cellobiose, 87.3 mg catalyst, and 25 mL of deionized water, was sealed and heated and kept at the desired temperature. Before sealing, N2 gas was passed into the solution for 30 min. The magnetic catalyst was recovered by magnetic separation, washed, and vacuum dried. Concentrations of cellobiose, glucose, fructose, and other products in the reaction solution were determined quantitatively by HPLC with an external standard method by comparing to a standard sample. The pH was adjusted with H2SO4 or NaOH. On a carbon basis, the conversion of cellobiose X was calculated as X = (C0 - Ct)/C0. The yield of the monosaccharide Y1 was calculated as Y1 = C1t/2C0. The yield of sucrose Y2 was calculated as Y2 = C2t/C0. The selectivity of glucose S was calculated as S = Y1/X, where C0, Ct are the concentrations of cellobiose at reaction times t = 0 and t, respectively, and C1t, C2t are the concentrations of the monosaccharide and sucrose at time t, respectively.
References:
Yang, Ren-Qiang;Zhang, Ni;Meng, Xiang-Guang;Liao, Xiao-Hong;Li, Lu;Song, Hong-Jin [Australian Journal of Chemistry,2018,vol. 71,# 8,p. 559 - 565]
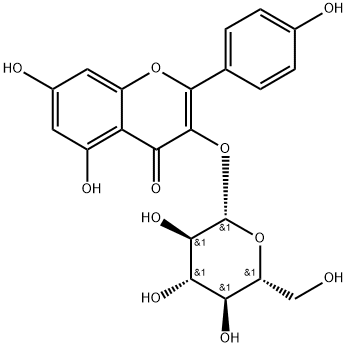
480-10-4
235 suppliers
$40.00/1mg

50-99-7
975 suppliers
$6.00/25g

13360-52-6
0 suppliers
inquiry
3458-28-4
526 suppliers
$10.00/5g

50-99-7
975 suppliers
$6.00/25g

141-46-8
31 suppliers
inquiry