The performance of diphenylphosphoryl azide
Jan 28,2022
Introduction
Diphenylphosphoryl azide, originally developed by Yamada in 1972[1], has shown significant synthetic versatility[2], being used in isocyanate synthesis, especially in the Curtius rearrangement, stereospecific conversion of alcohol into azide[3], as a coupling reagent in macrolactamization[4], in allylic amine synthesis[5], and in aziridination reactions[6]. Diphenylphosphoryl azide, also called DPPA, diphenyl phosphorazidate or phosphoric acid diphenyl ester azide, is a colorless liquid with high boiling point (157 °C/0.17 mmHg), and can be easily prepared by the reaction between diphenylphosphoryl chloride and sodium azide in acetone in high yield[7]. The Waldvogel group developed a reliable protocol for the large-scale (100 g) synthesis of DPPA, including purification by reduced-pressure distillation (Picture 1)[8]. A polymer-supported form of the reagent has also been developed using phenol resin by the Taylor group。

Picture 1 Preparation of DPPA in 400 mmol scale
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA)—a well-known azide reagent used in peptide couplings, Curtius rearrangements, and Mitsunobu inversions—is often encountered in pharmaceutical process development because it enables the most direct route to a desired product. Diphenylphosphonic azide acts as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides and phosphoramidates by reacting with amines. It is also used in the preparation of oligosaccharides linked with carbamate and urea bonds utilizing modified Curtis rearrangement. It is involved in pseudohalogen replacement of the azido group by treatment with nucleophilic reagents, such as water, butanol, ammonia, and various amines. Further, it is used as a hydroazidation catalyst for preparation of organoazides.
Different reactions by using DPPA
Diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) has been synthesized in microfluidics with near-100% yield in sub-3 minute residence time, affordably, and with a process design that minimizes hazards associated with hydrazoic acid (HN3) production. A pilot-plant scale continuous process for the on-demand synthesis of diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) that can readily be integrated with subsequent transformations was designed, built, and validated. Using Corning's Low Flow reactor system coupled to a membrane separator and in-line Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), DPPA was safely produced at a rate of 1 mol/hr as a 2.0 M anhydrous toluene stream[9]. Continuous FTIR was able to reliably monitor product quality, purity and concentration, showcasing the ease and utility of this continuous flow process for manufacturing common, safe pharmaceutical precursors.
(A) Yamada and co-workers developed an improved method for the curtius rearrangement reaction using DPPA, which was later named Yamada–Curtius rearrangement. In 2007, the Ciufolini group employed this method in the total synthesis of streptonigrone, to transform a carboxylic acid group into a protected amino group through the hydrolysis of an isocyanate intermediate, as the picture 2 showed [10].
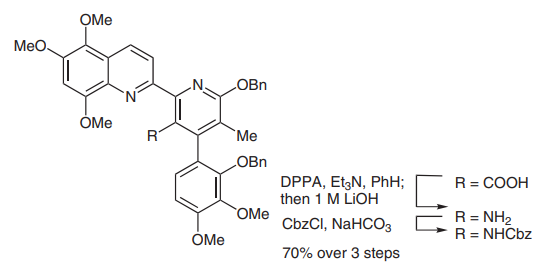
Picture 2 Curtius rearrangement reaction
(B) A primary or secondary alcohol can be easily converted into an azide group by DPPA under mildly basic conditions or using Mitsunobu conditions for stereochemical inversion. In the total synthesis of cribrostatin VI, the Danishefsky group successfully employed DPPA to displace a benzyl alcohol in high yield and ee[11]. Another example was demonstrated in the synthesis of Tamiflu and its phosphonate congeners by the Wang group in 2007 (picture 3 )[12].
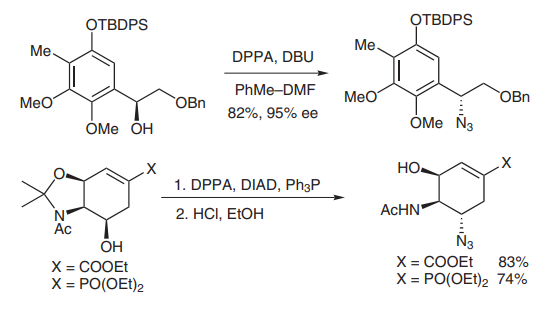
Picture 3 Substitution reaction
(C) Diphenylphosphoryl azide has also been widely used in peptide coupling reactions, particularly in macrolactamization (picture 4)[4]. In 2005, the Moody group completed the synthesis of thiopeptide amythiamicin D. In the final step, after global deprotection of N-Boc and tert-butyl groups, an a-amino ketone was successfully coupled with a thiazole carboxylic acid in DMF in 73% yield.1
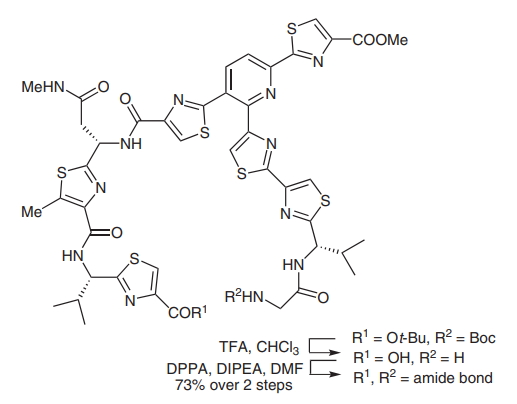
Picture 4 Peptide coupling reactions
(D) The Batey group has developed a stereoselective synthesis of allylic amines through a [3,3]-aza-phospha-oxa-Cope sigmatropic rearrangement[5]. Methylvinylcarbinol was converted into crotylamine in 85% yield over two steps. DPPA was used as an amine source in these reactions (picture 5), and excellent selectivity was achieved through addition of a catalytic amount of PdCl2(MeCN)2 catalyst.
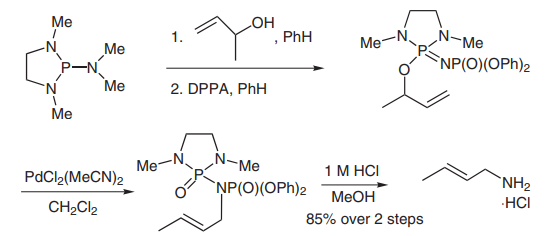
Picture 5 DPPA was used as an amine source
(E) A new catalytic aziridination reaction using cobalt tetraphenylporphyrin [Co(TPP)] as catalyst has been extensively studied by the Zhang group[6]. DPPA functioned as a nitrene source in the reaction that proceeded in good to excellent yield (picture 6).
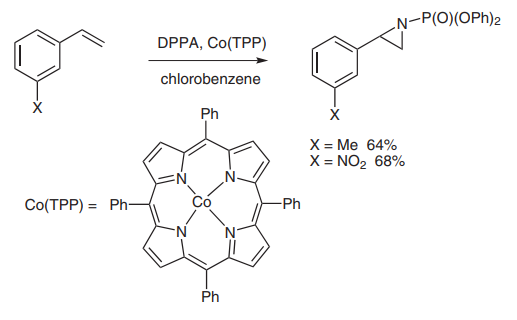
Picture 6 DPPA functioned as a nitrene source
Reference
1 Shioiri, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Yamada, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 6203.
2 Bräse, S.; Gil, C.; Knepper, K.; Zimmermann, V. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5188.
3 Thompson, A. S.; Humphrey, G. R.; DeMarco, A. M.; Mathre, D. J.; Grabowski, E. J. J. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 5886.
4 Han, S. Y.; Kim, Y. A. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2447.
5 Lee, E. E.; Batey, R. A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1865; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 1901.
6 Gao, G. Y.; Jones, J. E.; Vyas, R.; Harden, J. D.; Zhang, X. P. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 6655.
7 Hughes, R. A.; Thompson, S. P.; Alcaraz, L.; Moody, C. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15644
8 Wolff, O.; Waldvogel, S. R. Synthesis 2004, 1303.
9 Lu, Y.; Taylor, R. T. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 9267.
10 Chan, B. K.; Ciufolini, M. A. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8489.
11 Chan, C.; Heid, R.; Zheng, S.; Guo, J.; Zhou, B.; Furuuchi, T.; Danishefsky, S. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4596.
12 Shie, J. J.; Fang, J. M.; Wang, S. Y.; Tsai, K. C.; Cheng, Y. S. E.; Yang, A. S.; Hsiao, S. C.; Su, C. Y.; Wong, C. H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11892.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- A widely used coupling agent: Diphenylphosphoryl azide Dec 1, 2023
Diphenylphosphoryl azide is a well-known azide reagent used in peptide couplings, Curtius rearrangements, and Mitsunobu inversions
- What is Diphenylphosphoryl azide? Apr 19, 2021
Diphenylphosphonic azide acts as a reagent for the synthesis of peptides and phosphoramidates by reacting with amines. It is also used in the preparation of oligosaccharides linked with carbamate and urea bonds.
Hydroxytyrosol and its derivatives possess antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activities and beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system by preventing oxidative stress situations.....
Jan 28,2022APISodium acetate trihydrate is a promising heat storage material (m.p:58°C, heat of fusion, AHf~s:252 kJ/ kg (60.3 cal/g)....
Jan 28,2022APIDiphenylphosphoryl azide
26386-88-9You may like
Diphenylphosphoryl azide manufacturers
- Diphenylphosphoryl azide
-

- $2.00 / 200KG
- 2024-04-26
- CAS:26386-88-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500mt/year
- Diphenylphosphoryl azide
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2024-04-26
- CAS:26386-88-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 2000kg
- Diphenyl Azidophosphate (DPPA)
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg
- 2024-04-08
- CAS:26386-88-9
- Min. Order: 1Kg
- Purity: 99.9%
- Supply Ability: 200tons




