Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
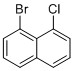
Synthesis and application of 1-bromo-8-chloronaphthalene
1-Bromo-8-Chloronaphthalene is usually readily prepared with a high yield via substitution of diazonium group by Halogens/Sandmeyer reaction. It is primarily used as an intermediate in the preparation
Jul 4,2022 APIMechanism of action of Pharmacodynamics
Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a phosphodiesterase inhibiting drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma under
Jul 1,2022 APIThe utility of chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol was the first of the clinically useful antibiotics to be synthesized and the only one which is marketed in synthetic form today
Jun 27,2022 APIThe synthesis of triethyl citrate
Triethyl citrate is a plasticizer of adhesive and sealant, with molecular formula of c12h20o7. It has strong solubility and good compatibility with many resins. The products plasticized with it have g
Jun 27,2022 APIUnique properties of ammonium dihydrogen phosphat
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, a chemical agent, also known as monoammonium phosphate, is a white crystal with the chemical formula of NH4H2PO4.
Jun 27,2022 APIProperties and structure of choline chloride
Choline chloride is an organic substance with the chemical formula C5H14CINO. It is white, hygroscopic crystal, tasteless and fishy. Melting point: 305 ℃
Jun 27,2022 APIBiological functions and synthesis of Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine functions as a neurotransmitter in the central, somatic, and autonomic nervous systems.
Jun 24,2022 APIA feed additive- l-threonine
L-threonine is an organic substance, the chemical formula is C4H9NO3, and the molecular formula is NH2-CH(COOH)-CHOH-CH3.
Jun 24,2022 APIsynthesis and Use of Histamine
Histamine is produced by basophils and mast cells and is involved in inflammatory responses.
Jun 23,2022 APISynthesis and Clinical implications of Melatonin
Melatonin is primarily secreted from the pineal gland. Melatonin is involved in synchronizing the sleep-wake cycle, blood pressure, and other circadian rhythms.
Jun 23,2022 API