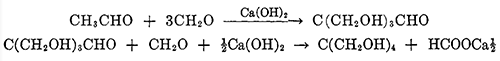Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Molecular structure data of 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate
2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate is an organic compound with the molecular formula C5H8O3. Colorless liquid. Soluble in general organic solvents and miscible with water.
May 31,2022 APIThe configuration of pentaerythritol
Pentaerythritol, or tetramethylolmethane, is the tetrahydric alcohol and when pure is a colorless crystalline material melting without decomposition at 263°C.
May 31,2022 APIAn excellent hydrogen energy carrier--methylcyclohexane
Among the cycloalkanes, methylcyclohexane (MCH) is the simplest alkylated cyclohexane and has been chosen as the model compound for surrogate fuels by many studies.
May 25,2022 APIThe manufacture of cyclohexanol
Cyclohexanol [108-93-0] is a colorless, viscous liquid with a camphoraceous odor.
May 25,2022 APISynthesis of Biotin
Biotin is an organic heterobicyclic compound that consists of 2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole having a valeric acid substituent attached to the tetrahydrothiophene ring.
May 24,2022 APISynthesis and Application of D-Penicillamine
D-Penicillamine (1) is a colorless crystalline powder with a weak odor typical of sulfur-containing amino acids, and a characteristic taste.
May 24,2022 APIThe biodegradability of diphenylamine
Diphenylamine (DPA) is a compound from the third European Union (EU) list of priority pollutants.
May 19,2022 APIUses and Mechanism of Vonoprazan
Vonoprazan (trade name Takecab) is a first-in-class potassium-competitive acid blocker. It was approved in the Japanese market in February 2015.
May 10,2022 APIUses of Arbidol hydrochloride
Arbidol hydrochloride is licensed in Russia and China mainly for treatment of influenza infection and other respiratory viral infections.
May 9,2022 APIUses and Side effects of Famotidine
Famotidine is used to treat and prevent ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
May 7,2022 API