What is N,N-Diisopropylethylamine?
Jun 29,2020
General Description
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is also known as Hunig’s base and abbreviated as DIPEA or DIEA, N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is a sterically hindered amine and an organic compound. The colourless liquid was named as Hung’s base after Siegfried Hunig, a German chemist. It is noteworthy that the compound is commercially available.
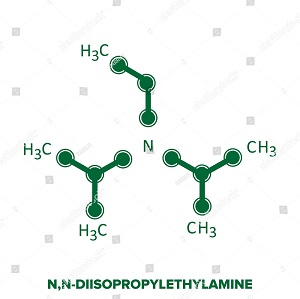
Structure & Reactivity
DIPEA consists of a central nitrogen that is bonded to an ethyl group and two isopropyl groups. A lone pair of electrons resides on the nitrogen atom, which can react with electrophiles. However, as the two isopropyl groups and the ethyl group occupy much of the space surrounding the nitrogen, only small electrophiles such as protons can react with the nitrogen lone pair.
DIPEA exhibits violent reaction as well as flammability with nitrates, oxidizing agents, and peroxides.
It can also react very exothermically and possibility of spitting with halogens and strong acids. In an alkaline environment, the compound is likely to react violently. In addition, the compound can form toxic products such as n-nitrosamines when combined with nitrous acid as well as oxygen, nitrosating agents, and nitrates.
Application
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is utilized as a base in the palladium(0)catalysed alkoxycarbonylation of both allyl acetates and phosphates . When treated with triphenyphosphine in the presence of DIPEA in ethanol under carbon monoxide pressure, diethyl-2-hexenyl phosphate produces mixtures of cisand trans--ethyl heptenoates in a ratio of 84:16. DIPEA is used as a neutralizer of the produced phosphoric acid. Notably, the alkyl ester cannot be produced without DIPEA.
When combined with boryl triflates, N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is hugely used in the enolate synthesis of ketones for application in directed cross-adol reactions . When reacted with Di-n-butylboryl Trifluoromethanesulfonate and DIPEA in ether, 4-methyl-2-pentanone generates unisolated baron enolate.
DIPEA is applied as a proton scavenger in organic synthesis. Since the compound is a sterically hindered amine, it lacks quaternization; therefore, making it a perfect choice of a base for use with extremely reactive alkylating agents. DIPEA is specifically useful as a base in the protection of alcohols as substituted ethers in the field of protecting group chemistry.
In the synthesis of peptides, the compound is also used in the coupling of amino acids. The steric nature and basicity of DIPEA during the coupling reaction affects the degree of racemization.
Utilization as a Reagent
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is a non-nucleophilic base commonly employed for substitution reactions. It acts as an activator for chiral iridium N, P ligand complexes, which can be utilized in the hydrogenation of α, β-unsaturated nitriles. The influence of varying concentration of N,N-diisopropylethylamine on the synthesis of olvanil in the presence of lipase catalyst has been investigated.
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine may be used in the synthesis of mannosylated ovalbumin peptides.
Proton scavenger used in peptide coupling, enolboration, Pd(0)-catalyzed alkoxycarbonylation of allyl phosphates and acetates, and as a catalyst in vinyl sulfone synthesis.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- How to synthesize N,N-Diisopropylethylamine Apr 15, 2024
N, N-diisopropylethylamine is an aliphatic sterically hindered amine.
- N,N-Diisopropylethylamine: Application, synthesis and toxicity Apr 11, 2023
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine is an organic compound and an amine consisting of a central nitrogen that is bonded to an ethyl group and two isopropyl groups, which is used in organic chemistry as a base.
See also
Edetic acid and EDTA. EDTA is white powder, which is soluble in sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate and ammonia solution, and 160 parts of boiling water, and slightly soluble in cold water.....
Apr 17,2020Organic Raw MaterialN,N-Diisopropylethylamine
7087-68-5You may like
- The Application and Synthesis of 3-Acetylpyridine
Oct 28, 2025
- Melamine: Overview, Neurotoxicity and its Mechanism
Oct 25, 2024
- What you need to know about ceramides?
Apr 17, 2024
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine manufacturers
- N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
-

- $0.00 / 200Kg/Drum
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:7087-68-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500mt
- N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:7087-68-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
-

- $1.10 / 1g
- 2025-11-18
- CAS:7087-68-5
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99.00%
- Supply Ability: 100 Tons Min






