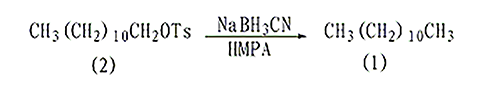Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Mechanism of action of Nicardipine
Nicardipine is a dihydropyridine-type CCB with highvascular selectivity,strong antihypertensive activity andcerebrovascular effects.
Apr 29,2022 APIMechanism of action of Nimodipine
Nimodipine is a dihydropyridine-type CCB used as anti-hypertensive agent.
Apr 29,2022 APIPasireotide for Cushing's disease
Pasireotide is a man-made protein that is similar to a hormone in the body called somatostatin. Pasireotide is used to treat Cushing's disease or acromegaly (endocrine disorders).
Apr 29,2022 APIPharmacokinetics of Enfuvirtide
Enfuvirtide (INN) is an HIV fusion inhibitor, the first of a class of antiretroviral drugs used in combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. It is marketed under the trade name Fuzeon
Apr 29,2022 APIImportant applications of 4'-methylacetophenone
4'-Methylacetophenone is a colorless or nearly colorless oily liquid that solidifies at a slightly lower temperature. Has a strong hawthorn-like aroma.
Apr 29,2022 APIThe preparation of cyanuric acid
Cyanuric acid, also known as cyanuric acid, chemical name is 2,4,6-trihydroxy-1,3,5-triazine; 2,4,6 trihydroxy-s-triazine (2,4,6-triazinettriol) ; sym-triazinetriol.
Apr 29,2022 APIThe preparation methods of dodecane
Dodecane is an organic compound with a chemical formula of C12H26 and a molecular weight of 170.33.
Apr 29,2022 APIHow to use (R)-1-phenylethylamine correctly
(R)-1-phenylethylamine is an organic compound with the molecular formula C8H11N.
Apr 29,2022 APIThe important role of 3-(methacryloyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane
3-(Methacryloyloxy)propyltrimethoxysilane is a versatile methacryloyloxysilane, and its molecular structure has a methacryloyloxy group containing an unsaturated double bond structure functional group
Apr 29,2022 APIToxicological information of decane
Decane refers to an alkane containing 10 carbon atoms and 22 hydrogen atoms in its molecular structure, the chemical formula is C10H22
Apr 29,2022 API