Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Pharmacological effects of empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is a type 2 sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT-2, sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter2) inhibitor jointly developed by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
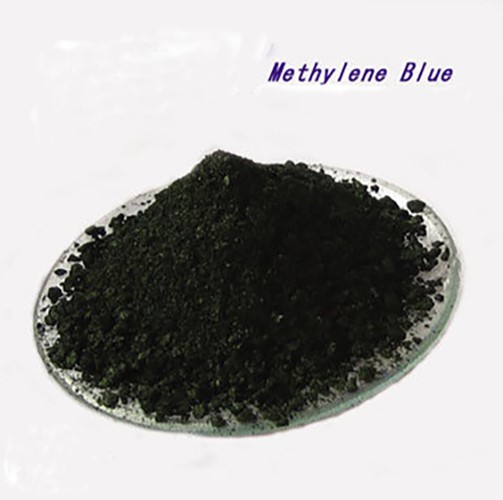
Apr 20,2022 APIApplications of Methylene Blue
The chemical formula of methylene blue is C16H18ClN3S, with a relative molecular weight of 319.85.
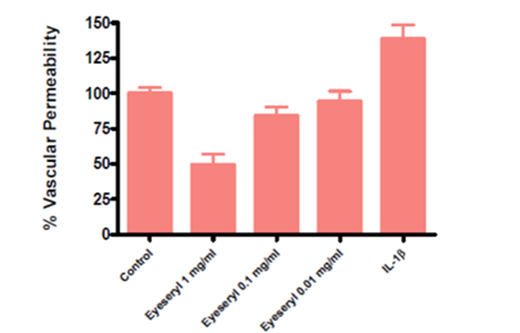
Apr 20,2022 APIThe important eye peptide of acetyl tetrapeptide-5
Acetyl tetrapeptide-5 is known as eye peptide and eye silk peptide. The molecular weight of acetyltetrapeptide-5 is 492.5 and the amino acid sequence is Ac- βAla-His-Ser-His-OH, the molecular formula
Apr 20,2022 APIThe properties and stability of butylamine
Butylamine is a chemical substance, the chemical formula of Butylamine is C4H11N. The appearance of Butylamine is a colorless transparent liquid without mechanical impurities.
Apr 20,2022 APIThe preparation method of iron chloride hexahydrate
Iron chloride hexahydrate is a reddish-brown to yellow hexagonal crystal, odorless, astringent, and deliquescent. Molecular formula of Iron chloride hexahydrate: FeCl3.6H2O.
Apr 20,2022 APIDifferent applications of thioglycolic acid
Thioglycolic acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C2H4O2S. Toxic, colorless and transparent liquid with strong pungent odor.
Apr 20,2022 APIAntibacterial properties of triclosan
The chemical name of triclosan is 5-chloro-2-(2',4'-dichlorophenoxy)phenol, the chemical formula is C12H7Cl3O2, and it is an organic compound.
Apr 20,2022 APIThe preparation of butyraldehyde
Butyraldehyde is a colorless, transparent, flammable liquid with a suffocating aldehyde odor. Slightly soluble in water, miscible with ethanol, ether, ethyl acetate, acetone, toluene and many other or
Apr 20,2022 APIThe synthetic method of n-hexadecane
N-hexadecane is a white solid or a colorless liquid. The melting point is 18.2°C, the boiling point is 286.79, the flash point is 135°C, the ignition point is 202°C
Apr 20,2022 APIUnique characteristics of Dipropylene glycol methyl ether
Dipropylene glycol methyl ether is an organic compound with a molecular formula of C7H16O3. Colorless viscous liquid with pleasant odor. Miscible with water and various organic solvents.
Apr 20,2022 API