리보플라빈
|
|
리보플라빈 속성
- 녹는점
- 290 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- 알파
- -135 º (c=5, 0.05 M NaOH)
- 끓는 점
- 504.93°C (rough estimate)
- 밀도
- 1.2112 (rough estimate)
- 굴절률
- -135 ° (C=0.5, JP Method)
- 인화점
- 9℃
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 물에는 아주 약간 녹고, 에탄올에는 거의 녹지 않습니다(96%). 특히 알칼리가 있는 경우 빛에 노출되면 용액의 품질이 저하됩니다. 다형성(5.9)을 보여줍니다.
- 물리적 상태
- 가루
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 1.7(at 25℃)
- 색상
- 노란색에서 주황색으로
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 5.5-7.2 (0.07g/l, H2O, 20°C)
- 냄새
- 약간의 냄새
- pH 범위
- 6
- 수용성
- 0.07g/L(20℃)
- 감도
- Light Sensitive
- Merck
- 14,8200
- BRN
- 97825
- BCS Class
- 1
- 안정성
- 안정적이지만 빛에 민감합니다. 강한 산화제, 환원제, 염기, 칼슘, 금속염과 호환되지 않습니다. 습기에 민감할 수 있습니다.
- InChIKey
- AUNGANRZJHBGPY-SCRDCRAPSA-N
- LogP
- -2.009 (est)
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 83-88-5(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST
- Riboflavine(83-88-5)
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | F,T | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 11-23/24/25-39/23/24/25 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 24/25-45-36/37-16 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution | ||
| WGK 독일 | 1 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | VJ1400000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 8-10-21 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS 번호 | 29362300 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 83-88-5(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 in rats (g/kg): >10 orally, 5.0 s.c., 0.56 i.p. (Unna, Greslin) | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-11845 |
리보플라빈 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
리보플라빈, 일컬어 비타민 B2는와 먼저 G로 알려져 있는 비타민이고, 인간과 다른 동물에 있는 유지 건강에 있는 핵심 역활을 가진 쉽게 흡수한 착색한 미량 영양소입니다. 비타민 B2는 다양한 세포질 과정을 위해 요구됩니다. 그것은 에너지 물질 대사에 있는, 그리고 지방, 키톤체, 탄수화물 및 단백질의 물질 대사를 위한 핵심 역활을 합니다.용도
리보플라빈 (비타민 B2)는 병 후에 나이 든 유아, 임신부, 모유로 기르는 어머니, 환자 및을 위한 자양물로 정상적인 생존에 있는 유기체를 위한 근본적인 필요성입니다.그것은 carbonhydrate, 단백질 및 지방의 물질 대사에, 포함하고, 참가하고, 풍미 단백질의 중요한 구성, 수소의 옮기는 효소 체계입니다. 임상 연습에서는, 그것은 perleche, 설염, ophthalmitis, 결막염, seborrhea, 적당한 효력을 가진 음낭 염증에 적용 가능합니다, 음식과 급식 기업에서, 그것 음식과 급식 첨가물로 널리 이용되고 증명해 달라고 합니다 정결하것을.
순도시험
(1) 비선광도 : 이 품목을 차광하여 105℃에서 2시간 건조한 다음 약 50mg을 정밀히 달아 0.1N 수산화나트륨용액 2mL를 가하여 녹이고 새로 끓여서 식힌 물 5mL를 가한 다음 액을 충분히 흔들어 섞으면서 알데히드를 함유하지 않은 에탄올 2mL를 가하고 새로 끓여서 식힌 물을 가하여 10mL로 하여 30분 이내에 이 액의 선광도를 측정할 때, 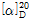 =-120~-140°이어야 한다.
=-120~-140°이어야 한다.
(2) 루미플라빈 : 이 품목 25mg에 알콜을 함유하지 않은 클로로포름 10mL를 가하여 5분간 흔들어 섞은 다음 여과할 때, 그 색은 0.1N 중크롬산칼륨용액 3mL에 물을 가하여 1,000mL로 한 액의 색보다 진하여서는 아니 된다.
(3) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(4) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 2.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(5) 카드뮴 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(6) 수은 : 이 품목을 수은시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(7) 비술폰화방향족제1급아민 : 색소시험법 중 비술폰화방향족제1급아민시험을 할 때, 그 양은 아닐린으로서 0.01% 이하이어야 한다.
확인시험
이 품목 1mg을 물 100mL에 녹인 액은 엷은 황록색으로서 강한 황색을 띤 녹색의 형광을 발하고 이 형광은 묽은염산 또는 수산화나트륨시액을 가하면 없어진다.
정량법
이 품목을 건조한 다음 약 0.015g을 정밀히 달아 빙초산(1→400) 800mL를 가하여 60~70℃로 가열하여 녹이고 식힌 다음 물을 가하여 1,000mL로 하고 이를 시험용액으로 한다. 따로 비타민B2표준품을 사용하여 검체의 경우와 같이 처리하여 표준용액을 만들어 물을 대조로 하여 파장 445nm에서 시험용액의 흡광도 AT 및 표준용액의 흡광도 AS를 측정한 다음 즉시 각각 그 액에 히드로설파이드나트륨 0.02g을 가하여 흔들어 섞어 탈색시키고 그 액의 흡광도 AT'' 및 As''를 측정하여 다음 계산식에 따라 비타민B2(C17H20N4O6)의 함량을 구한다. 다만, 모든 조작은 직사광선을 피하고 차광용기를 사용하여야 한다.
강열잔류물
이 품목의 강열잔류물은 0.3% 이하이어야 한다.
개요
A water-soluble B fraction was found in the 1920s to contain a yellow, fluorescent growth factor called riboflavin in England and vitamin G in the United States. In the early 1930s, several groups found the coenzyme forms of riboflavin 50-phosphate (flavin mononucleotide) and the further conjugate with adenylic acid (flavin adenine dinucleotide).화학적 성질
VITAMIN B2 (Riboflavin). Some earlier designations for this substance included vitamin G, lactoflavin, hepatoflavin, ovoflavin, verdoflavin. The chemical name is 6,7-dimethyl-9-d-l’ribityl isolloxazine. Riboflavin is a complex pigment with a green fluorescence.물리적 성질
Riboflavin is moderately soluble in water (10–13 mg/dl) and ethanol but insoluble in ether, chloroform, and acetone. It is soluble but unstable under alkaline conditions.The catalytic functions of riboflavin are carried out primarily at positions N-1, N-5, and C-4 of the isoalloxazine nucleus. In addition, the methyl group at C-8 participates in covalent bonding with enzyme proteins. The flavin coenzymes are highly versatile redox cofactors because they can participate in either one- or two electron redox reactions
Riboflavin antagonists include analogs of the isoalloxazine ring (e.g., diethylri boflavin, dichlororiboflavin) and the ribityl side chain (e.g., d-araboflavin, d-galactoflavin, 7-ethylriboflavin).
용도
riboflavin (Vitamin B2) is used in skin care preparations as an emollient. It can be found in sun care products as a suntan enhancer. Medicinally, it is used for the treatment of skin lesions.정의
ChEBI: D-Ribitol in which the hydroxy group at position 5 is substituted by a 7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydrobenzo[g]pteridin-10(2H)-yl moiety. It is a nutritional factor found in milk, eggs, malted barley, liver, kidney, heart, and leafy vege ables, but the richest natural source is yeast. The free form occurs only in the retina of the eye, in whey, and in urine; its principal forms in tissues and cells are as flavin mononucleotide and flavin-adenine dinucleotide.일반 설명
The conflicting results were eventually found to be due,in part, to deficiencies in study animals not just of vitamin B2,but also vitamin B3 (niacin), the cause of human forms of pellagra,and/or vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), another cause of dermatitis.Likewise, treatments with vitamin B2 were inconsistentbecause the early sources of this vitamin contained otherB vitamins. Vitamin B2 was eventually isolated from eggwhites in 1933 and produced synthetically in 1935. Thename riboflavine was officially accepted in 1960; althoughthe term was in common use before then. In 1966, IUPACchanged it to riboflavin, which is in common use today.Riboflavin is synthesized by all green plants and by mostbacteria and fungi. Therefore, riboflavin is found, at least insmall amounts, in most foods. Foods that are naturally highin riboflavin include milk and other dairy products, meat,eggs, fatty fish, and dark green vegetables.Chemically, riboflavin is an N-glycoside of flavin, alsoknown as lumichrome, and the sugar, ribitol .Flavin is derived from the Latin word flavus for “yellow”because of the yellow color of its crystals and yellow fluorescenceunder UV light. Riboflavin is heat stable but easilydegraded by light. Its systematic names are 7,8-dimethyl-10-ribitylisoalloxazine and 7,8-dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)isoalloxazine.
Clinical Use
Severe riboflavin deficiency is known as ariboflavinosis, andtreatment or prevention of this condition is the only provenuse of riboflavin. Ariboflavinosis is most commonly associatedwith multiple vitamin deficiency as a result of alcoholismin developed countries. Because of the large numberof enzymes requiring riboflavin as a coenzyme, deficienciescan lead to a wide range of abnormalities. In adults seborrheicdermatitis, photophobia, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, andoropharyngeal changes including angular stomatitis, glossitis,and cheilosis, are often the first signs of riboflavin deficiency.In children, cessation of growth can also occur. As the deficiencyprogresses, more severe pathologies develop untildeath ensues. Riboflavin deficiency may also produce teratogeniceffects and alter iron handling leading to anemia.Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal and subcutaneous routes. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.환경귀착
Physicochemical PropertiesRiboflavin has the appearance of a yellow to orange amorphous solid and imparts an orange color to the B vitamin tablets. Riboflavin has a melting point of 290°C, a density of 1.65, and a refractive index of 135°. The pKa is 9.888 and log P is 0.095. Riboflavin has solubility in water of 0.1 g l-1.
Exposure Routes and Pathways
The route of exposure is oral. Dietary sources of riboflavin and its coenzymes include broccoli, spinach, asparagus, enriched flour, yeast, eggs, milk, cheese, mackerel, trout, poultry, liver, and kidneys.
Toxicokinetics
Riboflavin, which is only moderately water soluble, is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but is limited to about 27 mg at any one time from an oral dose given to an adult. Hence, mega doses would not be expected to increase significantly the total amount absorbed. It is hepatically metabolized, protein bound, and widely distributed to tissue; however, little is stored in the liver, spleen, heart, and kidneys. Riboflavin is excreted renally as metabolites, which have been oxidatively cleaved in the ribityl side chain and converted to hydroxymethyls in the ring methyl functions. Riboflavin in excess of daily body needs is excreted unchanged in the urine. Riboflavin exhibits biphasic pharmacokinetics with initial and terminal half-lives of 1.4 and 14 h, respectively.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from H2O as a yellow-orange powder in three different forms with differing amounts of H2O. It melts if placed in an oil bath at 250o, but decomposes at 280o if heated at a rate of 5o/minute. It is also purified by crystallisation from 2M acetic acid, then extracted with CHCl3 to remove lumichrome impurity. [Smith & Metzler J Am Chem Soc 85 3285 1963.] Its solubility in H2O is 1g in 3-15L depending on the crystal structure. Its solubility in EtOH at 25o is 4.5mg in 100mL. Store it in the dark because it is decomposed to lumichrome by UV light. [Pearson The Vitamins vol V pp1-96 1967 and vol VII pp 1-96 1972, Gy.gy and Pearson eds, Academic Press, Beilstein 26 IV 2542.]리보플라빈 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
리보플라빈 공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHANDONG ZHI SHANG CHEMICAL CO.LTD | +86 18953170293 |
sales@sdzschem.com | China | 2931 | 58 |
| TAIZHOU YUXIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO,.LTD | +86-576-88902229;+86-0576-88902229 +8613968687450 |
yuxin@yuxchem.com | China | 122 | 58 |
| XI AN SGONEK BIOLOGICAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD | 15202951039 |
jason@sgonekbio.com | China | 268 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618740459177 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 902 | 58 |
| Hebei Yime New Material Technology Co., Ltd. | +86-66697723 +86-17703311139 |
admin@china-yime.com | China | 563 | 58 |
| XI'AN TIANGUANGYUAN BIOTECH CO., LTD. | +86-029-86333380 18829239519 |
sales06@tgybio.com | China | 959 | 58 |
| shandong perfect biotechnology co.ltd | +86-53169958659; +8618596095638 |
sales@sdperfect.com | China | 294 | 58 |
| Henan Tengmao Chemical Technology Co. LTD | +8615238638457 |
salesvip2@hntmhg.com | China | 415 | 58 |
| Hangzhou ICH Biofarm Co., Ltd | +undefined8613073685410 |
sales@ichemie.com | China | 985 | 58 |
| Wuhan Marco Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | +86-86-18572802410 +8618572802410 |
sales@marcopht.com | China | 55 | 58 |









